Background and overview[1][2]
3-Chloropropiophenone is a key intermediate in the synthesis of bupropion hydrochloride, dapoxetine, maraviroc and other drugs. Bupropion hydrochloride is an antidepressant that blocks the absorption of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine by weak neurons. It is suitable for patients who have unclear effects on other depressants or who cannot tolerate depression. At the same time, bupropion hydrochloride Bupropion may also be used as an auxiliary treatment for smoking cessation, viral infections, or sexual dysfunction.
Maraviroc was developed by Pfizer and approved by the US FDA on August 6, 2007. Maraviroc is a CCR5 receptor antagonist. CCR5 receptor is the only pathway for HIV infection. Therefore, it can be used as a broad-spectrum anti-HIV drug for clinical use in combination with other antiretroviral drugs. Treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults.
Apply[1]
3’-Chloropropiophenone is a key intermediate in the synthesis of bupropion hydrochloride, dapoxetine, maraviroc and other drugs.
1. Preparation of 3-chlorophenylpropanol.
As an important intermediate in the synthesis of dapoxetine, 3’-chlorophenylpropanol plays a key role in the cost and quality of the entire drug. Reports on the synthesis of R-3’-chlorophenylpropanol mainly focus on using 3’-chlorophenylpropanol as raw material and using a reducing agent to synthesize the target product.
Using tetrahydrofuran as the solvent and spiroboron ester compounds as the catalyst, the target compound is synthesized. This process has high solvent and catalyst costs. Using 95% ethanol as the solvent and potassium borohydride as the reducing agent, the cost is low. However, the synthesized product is a mixture and needs to be separated before the target product can be formed. The final overall yield is low, resulting in high costs. DMSO is used as the solvent, and chiral catalysts are uncommon and the cost is high. The post-processing is complicated and consumes a lot of energy. Use ethylene glycol dimethyl ether as the solvent and sodium borohydride as the reducing agent. The solvent cost is high, and the product is a mixture that needs to be split.
In summary, in the synthesis process of R-3′-chlorophenylpropanol, there are common shortcomings such as high cost of solvents and reducing agents, difficult post-processing, difficult to control the reaction process, low selectivity, and low chiral purity. . In summary, the research on the synthesis process of R-3′-chlorophenylpropanol and the development of a production process with lower cost, convenient processing and better product quality are of great significance to the synthesis of the above drugs and the treatment of related diseases. At the same time It has broad market prospects.
The process of synthesizing 3′-chlorophenylpropanol using 3-chloropropiophenone, the specific steps are as follows:
1) Add 3’-chloropropiophenone and L-prolinol to 95% ethanol in sequence and stir;
2) Cool the reaction solution after it is completely dissolved;
3) Add potassium borohydride into the reaction solution in batches, and keep warm after completion;
4) After heating the reaction solution to reflux, concentrate the reaction solution under reduced pressure;
5) Add n-hexane to the reaction solution, heat it, and then add activated carbon for heat preservation and decolorization;
6) Filter the reaction solution, rinse the filter cake with 500-700ml n-hexane, and collect the filtrate;
7) Crystallize and filter the filtrate, rinse the filter cake once with 300-500ml n-hexane, and dry it under vacuum to obtain 3′-chlorophenylpropanol.
2. Prepare a maraviroc intermediate.
The method includes steps:
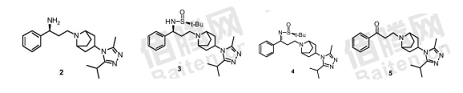
1) Make 3-chloropropiophenone and 3-(3-isopropyl-5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-8-azabicyclo [3.2. 1] Octane reacts to obtain a compound with a structure shown in Formula 5;
2) React the compound with the structure shown in Formula 5 and the chiral auxiliary (S)-tert-butylsulfenamide to generate the compound with the structure shown in Formula 4;
3) Reducing the compound with the structure shown in Formula 4 to obtain the compound with the structure shown in Formula 3; and
4) (S)-3-((3-isopropyl-5-methyl-4H-1,2, 4-triazole-4-) obtained by hydrolyzing the compound shown in formula 3 (base)-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-8-yl)-1-phenylpropylamine hydrochloride is treated with an alkaline solution to obtain a compound with a structure shown in Formula 2;
Preparation[3]
Method 1: Obtained by diazotization and chlorination of meta-aminopropiophenone and sodium nitrite. The molar ratio between meta-aminopropiophenone and sodium nitrite is 1:1~1:1.2, and the reaction equation is for:

The specific operation steps are: add m-aminophenone and an appropriate amount of hydrochloric acid into the reaction kettle, stir and cool to 0°C, add sodium nitrite aqueous solution dropwise, control the temperature at 0~5°C, and use starch potassium iodide test paper to detect excess In the presence of nitrous acid, under stirring, add the diazonium salt solution to the pre-prepared cuprous chloride solution that has been cooled to 0°C to obtain crude 3′-chloropropiophenone. First, wash it with hydrochloric acid and water. times, then wash with 5% sodium carbonate solution, and finally wash with water, dry, and distill under reduced pressure to obtain a product with a yield of about 60.5% and a content of 90% to 95%.
Method 2: Use chlorination of phenylacetone to obtain 3′-chloropropiophenone. The chemicals used in this method are: phenylacetone, metal trichloride salt, solvent A, chlorine Cl2, of which solvent A is both It can dissolve phenyl acetone and be miscible with metal trichloride salt. The reaction equation is:

The steps are as follows:
The first step, ���Add appropriate amounts of metal trichloride and solvent A to the reaction kettle, add phenyl acetone solution dropwise while stirring, pass in chlorine Cl2, and perform chromatography to track the reaction in the temperature range of 15 to 70°C, about 6 to Stop chlorine supply after 10 hours;
The second step, low temperature hydrolysis;
The third step, washing and layering;
The fourth step is distillation under reduced pressure to obtain the target crude product;
The fifth step is to distill the crude product at a temperature of about 170°C to obtain a fine product with a content of 99.7% to 99.9%; the yield is 88% to 90%;
Main reference materials
[1] CN201610255249.6. Maraviroc intermediate and preparation method thereof
[2] CN201810278275.X. A synthesis process of 3′-chlorophenylpropanol
[3] CN200410065482.5. A method for preparing 3’-chloropropiophenone



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
