[Background and Overview][1][2]
Late blight and downy mildew are important diseases of crops in the world, and their prevention and treatment have attracted the attention of scientific researchers from all over the world. A new fungicide, fenthiocarb, jointly developed by Combination Chemical Industry Corporation and Ihara Corporation, has good activity against oomycete fungal diseases. Benthiostrobin can also be made into a mixture with mancozeb and fenfoside. The generic name of benthiavalicarb-isopropyl is KIF-230, KU F.1004. Its chemical name is {(s)-1-[(R )-1-(6-fluorobenzothiazol-2-yl)ethylcarbamoyl]-2-methylpropyl}carbamate isopropyl. CAS accession number is 177406-68-7. Benthiostrobin has good bactericidal activity against Phytophthora, and has a good inhibitory effect on the formation and germination of sporangia at low concentrations, but it has a good inhibitory effect on the release of zoospores and the germination of zoospores. movement has no effect.
Field trials on grape downy mildew, melon downy mildew and cruciferous downy mildew showed similar results. Benthiostrobin has bactericidal activity against potato late blight and melon downy mildew. Tests have proven that the new fungicide Benthiostrobin has strong preventive, therapeutic and penetrating activities, as well as good persistence and erosion resistance. In field trials, benzostrobin was formulated into a mixture with other fungicides at a lower dose (25 to 75 grams of active ingredient per hectare), which also had very good efficacy against the pathogen. In order to achieve broad spectrum Due to its high activity and low residue, it is recommended to formulate a mixture with other fungicides for application. Benthiostrobin has outstanding performance in toxicology and environmental protection, and it will not cause toxicity to plants when applied at the prescribed dosage.
[Property][3]
The pure product of Benthiostrobin is a white powder solid with a melting point of 152cc; the industrial product is an off-white powder with a melting point of 153.1~169.5cc, vapor pressure < 3.0X10-Pa (25cc); relative density 1.25 (20.5cc) ;The distribution coefficient KowlogP is 2.52. Solubility in water: 13.14 m g/L (20 ℃).
[Specifications][3]
Single doses are available as 15% water-dispersible granules. The mixture is a mixture of water-dispersible granules with chlorothalonil, 5% fenthiostrobin + 50% chlorothalonil.
【Usage and Dosage】[3]
Benthiostrobin has strong prevention, treatment and penetration effects, and has good persistence and resistance to rain erosion. According to the test results, the mixture of Benthiostrobin and other fungicides is a very good agent, such as Mancozeb, Fossil, etc. At a lower dose of 25-75ga.i./ hm 2, Benthiostrobin can effectively control downy mildew on grapes, cucumbers and cabbage, as well as late blight on potatoes, tomatoes, vegetables and grapes. It is recommended to mix Benthiostrobin and Chlorothalonil. The recommended diseases and usage methods of this mixture are as follows:

[Pharmacological effects][3]
The mechanism of action is still under study, but it is completely different from electron transport inhibitors or RNA synthesis inhibitors. It does not affect the oxidation and synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, and is estimated to be a cell wall synthesis inhibitor. Tests have also shown that Benthiostrobin is effective against potato late blight, which is resistant to amide fungicides, and cucurbit downy mildew, which is resistant to methoxyacrylates. Tests have shown that Benthiostrobin is highly active against oomycete pathogens such as blight and downy mildew at a concentration of 1 mg/L, but is ineffective against other pathogens, showing high selectivity. At the same time, Benthiostrobin can penetrate from the leaf surface to the inside of the leaf, or from the inside of the leaf to the leaf surface. It has good permeability, so it has both preventive and therapeutic effects. In addition, Benthiostrobin also has the characteristics of inhibiting secondary infection of pathogens, and has excellent long-lasting effect and rain resistance.
[Adverse reactions][3]
The acute toxicity of benthiostrobin is: acute oral LDso in rats and mice (male and female) > 5000 mg/kg; acute percutaneous LDs0 in rats (male and female) > 2000 mg/kg; Rat acute inhalation 0(4h) > 4.6 mg/L. It has no irritating effect on the skin and eyes of rabbits and is non-allergenic to the skin of guinea pigs. The Ames test is negative and has no teratogenic or carcinogenic properties. Toxicity to aquatic organisms LC uranium (96 h, mg/L) is: rainbow trout > 10, bluegill sunfish > 10, carp > 10, water fleas > 10. There is no adverse effect on silkworms at 75 to 150 mg/L. For bees, LJ D50 (48 h) is 100 g/head (oral, contact). For earthworms LC Uranium(14d) > 1000 m g/kg soil.
【Preparation】 [4]
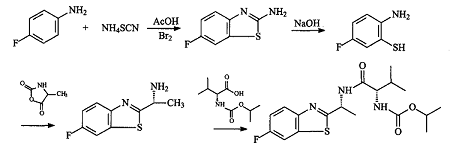
Method 1: Add bromine dropwise to p-fluoroaniline and ammonium thiocyanate in acetic acid solvent to obtain 2-amino 6-fluorobenzothiazole, and then hydrolyze in 50% sodium hydroxide solution to obtain key intermediate 2 -Amino-5-fluorothiophenol, obtained by reacting 2-amino-5-fluorothiophenol with alanine 4-carbonyl anhydride-4-methyl-1,3-oxazoline.2,5.dione 1-(6-Fluoro-2-benthiazole)ethylamine is then reacted with IV isopropylcarbonyl and valine to obtain the target product benthiazole. This route uses glacial acetic acid as the solvent when synthesizing 2-amino-6-fluorobenzothiazole. Since the reaction temperature is required to be 8 to 10°C, the reaction solution is easy to freeze, making the operation difficult, and glacial acetic acid is difficult to recycle. . In addition, this route also has the hydrolysis of 2-amino-6-fluorobenzothiazole.The disadvantage of 2-amino-5-fluorothiophenol is that it is easily oxidized.
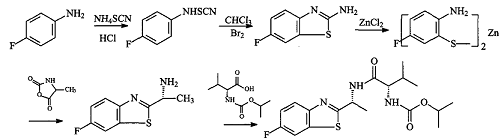
Route 2: p-fluoroaniline and ammonium thiocyanate under the action of hydrochloric acid first generate 4-fluorophenylthiourea, and then add bromine dropwise to the chloroform solution to obtain 2-amino-6-fluorobenzothiazole, avoiding Route 1: It is easy to freeze during the reaction, and chloroform is easy to recycle. 2-Amino-6-fluorobenzothiazole reacts with zinc chloride during the hydrolysis process to form 2-amino-5-fluorobenzothiophene zinc salt. This salt is a coordination compound of zinc and is not easily oxidized in the air. .
[Main reference materials]
[1] Chen Qihui. New fungicide Benthiostrobin[J]. Pesticides, 2004, 43(11): 515-517.
[2] Liu Yunping, Yang Jichun, Chai Baoshan, et al. New fungicide fenthiostrobin[J]. Pesticides, 2011, 50(10): 756-758.
[3] Feng Huacheng. Novel fungicide benthiavalicarb-isopropyl[J]. World Pesticides, 2008, 30(3): 51-51.
[4] Yang Fang, Liao Daohua, Shi Wenjuan, et al. Synthesis of fenthiostrobin[J]. Pesticides, 2010, 49(3): 174-175+ 178.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
