[Background and Overview][1][2][3]
As clinicians’ understanding of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease (coronary heart disease) gradually deepens, its treatment methods are also constantly improving. Conservative drug treatments (such as antiplatelet, thrombolysis, beta-blocker agents, calcium antagonists, nitrate preparations, lipid-lowering therapy) and interventional therapy have become the main methods for the current treatment of coronary heart disease. However, the above-mentioned drugs mainly exert myocardial protection effect indirectly by improving the oxygen supply and demand balance of ischemic myocardium. Therefore, patients still have symptoms or signs of heart failure after treatment, and the clinical efficacy is limited.
Trimetazidine is a piperazine derivative and a new type of anti-myocardial ischemia drug. It mainly inhibits myocardial fatty acid β-oxidation by inhibiting 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, increases glucose oxidation, and improves glucose metabolism. Glycolysis is coupled with glucose oxidation to optimize energy metabolism of cardiomyocytes. A large number of basic studies have confirmed that trimetazidine hydrochloride can reduce the overload of intracellular H+, Na+, and Ca2+ and inhibit oxygen freedom. It generates base, stabilizes the functional status of mitochondrial membrane, has various cell protective effects such as antioxidant and anti-apoptosis, and does not affect hemodynamics and has no side inotropic effects. Its good pharmacological effects are increasingly favored by clinicians. Trimetazidine hydrochloride is a new drug that improves myocardial energy metabolism. Its therapeutic effect in heart failure has been confirmed. It has no obvious side effects, has good treatment tolerance, is safe and reliable, and is worthy of clinical promotion and application. However, there is little clinical data on treating patients’ arrhythmia, improving patient mortality, and adverse effects of long-term use, and further research is needed. There are currently 8 main types of trimetazidine impurities detected, including trimetazidine impurity A, trimetazidine impurity B, trimetazidine impurity C, trimetazidine impurity D, trimetazidine impurity E, Trimetazidine Impurity F, Trimetazidine Impurity G, Trimetazidine Impurity H, Trimetazidine Impurity I, may originate from process impurities, reaction by-products and unreacted starting materials and intermediates in the raw materials. bodies and reagents, etc. With the improvement of the quality of life, people pay more and more attention to drug safety, and impurities in drugs are directly related to the quality of drugs. The “Technical Guiding Principles for Research on Impurities in Chemical Drugs” systematically stipulates the analysis of impurities and the rapid characterization of impurities. It has good guiding significance for quality control and process optimization of the R&D process.
[Structure][4]
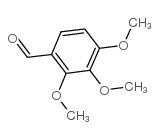
Trimetazidine impurity C, chemical name 2,3,4-trimethoxybenzaldehyde, Chinese alias trimethoxybenzaldehyde, white to off-white crystalline powder, CAS number 2103-57-3, molecular formula C10H12O4, molecular weight 196.20000, density 1.133g/cm3, melting point 38-40 °C (lit .), boiling point 168-170 ºC at 760mmHg, flash point >230 °F, refractive index 1 n20/D 1.5547(lit.), structural formula is as follows:
【Synthesis】[3][5]
The synthesis of trimetazidine impurity C is as follows:
Method 1: Using the gallic acid derivative 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzaldehyde as the main raw material, dimethyl sulfate as the alkylating agent, in the presence of the phase transfer catalyst quaternary ammonium salt and sodium hydroxide, pass O-alkylation method is used to carry out methylation reaction, and the chemical reaction formula is as follows:
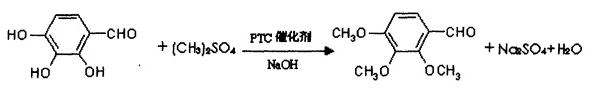
Control the reaction temperature to 50-70°C. After the reaction, the material is left to stand and stratified. The upper oily substance is washed with water until neutral, distilled under reduced pressure, and refined to obtain a white crystalline powder, which is the product trimetazidine impurity C. The alkylating agent dimethyl sulfate, catalyst quaternary ammonium salt and sodium hydroxide are added in batches to complete the methylation reaction in multiple stages; the weight ratio of each material is as follows: 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzaldehyde: Dimethyl sulfate:PTC catalyst=1:3~4:0.08~0.1. The feeding plan makes the 2,3,4-trimethoxybenzaldehyde product yield reach 88%; using a new phase transfer catalyst, the reaction conditions are mild and the purity reaches more than 99%. The high-purity product can ensure that this product can be used as an intermediate for pharmaceutical production. body reliability. The preparation process is simple, the equipment investment is low, and the process conditions are easy to control, which provides convenience for industrial production. The gallic acid derivative 2,3,4-trihydroxybenzaldehyde, the raw material of the present invention, can be prepared by using gallnut, a natural forest product, as the initial raw material. my country is rich in natural forest product resources and the cost is greatly reduced. Gallic acid is extracted from gallnuts and the product prepared by the invention is obtained through a synthesis method. Its market price is increased by more than 10 times and considerable economic benefits can be achieved.
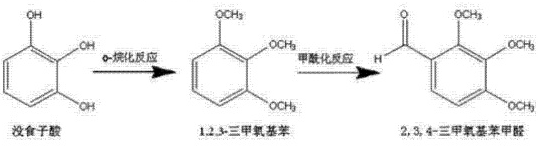
Method 2: A method for preparing pharmaceutical intermediate 2,3,4-trimethoxybenzaldehyde (trimetazidine impurity C), including the following steps:
1) Using pyrogallic acid as the raw material and dimethyl sulfate as the alkylating reagent, methylation is carried out through O-alkylation reaction in the presence of sodium hydroxide. The weight ratio of each material input: pyrogallic acid Acid: dimethyl sulfate: 30% sodium hydroxide solution = 1:3.3-4:4, reaction temperature 30-60°C, preferably incubated for 30 minutes. After the reaction is completed, separate layers, take the upper oil layer, wash it with water until neutral, and get the middle To form 1,2,3-trimethoxybenzene, dimethyl sulfate and sodium hydroxide are preferably fed in batches to complete the methylation reaction in multiple stages.
2) Convert the value obtained in step 1)The intermediate 1,2,3-trimethoxybenzene is formylated with the Vilsmeier-Haack reagent. The Vilsmeier-Haack reagent is a mixture of DMF and phosphorus oxychloride. The ratio of the two is arbitrary. DMF is preferred: phosphorus oxychloride = 1:2, control the reaction temperature to 70-80°C, preferably keep the temperature for 10 hours. After the reaction is completed, hydrolyze, extract with ethyl acetate, distill under reduced pressure, and cool the effluent to crystallize the product. The weight ratio of each material is preferably 1, 2, 3 -Trimethoxybenzene:DMF:phosphorus oxychloride=1:1:2. The synthesis route is shown below:
[Application][2][3][5]
2,3,4-Trimethoxybenzaldehyde is an important pharmaceutical intermediate and can be used in the synthesis of new drug Ca2+ channel blockers. This drug can be selectively used on cerebral arteries to reduce the incidence of headaches, and there is a certain demand in the European and American markets. It can also be used as impurity C of trimetazidine, which can be used in the formulation of standards during the research and development of trimetazidine. The study of impurities is an important part of drug research and development. It includes selecting appropriate analytical methods, accurately identifying and measuring the content of impurities, and determining reasonable limits of impurities based on the results of pharmaceutical, toxicological and clinical studies. This research occurs throughout the entire process of drug development. Adverse reactions caused by drugs in clinical use are not only related to the pharmacological activity of the drug itself, but also related to impurities in the drug. For example, polymer impurities such as polymers in antibiotics such as penicillin are the main cause of allergies. Therefore, conducting impurity research in a standardized manner and controlling impurities within a safe and reasonable range will be directly related to the quality and safety of marketed drugs. In the process of research and development of trimetazidine generic drugs, it is necessary to conduct a detailed study on the quality of products of the same type that have been launched, analyze the types of impurities, including trimetazidine impurity C and its content, and conduct a comprehensive quality review with the products under development. By comparison, the impurity limits of the product under development are formulated based on this, including the limit of impurity C of trimetazidine.
[References]
[1] Zhang Ying, Shi Dazhuo. Research progress on trimetazidine optimizing myocardial metabolism[J]. Medical Review, 2015, 21(13): 2313-2316.
[2] Xia Mingwei, Ma Likun. Progress in the clinical application of trimetazidine in cardiovascular diseases[D]. , 2008.
[3] Zhang Zonghe; Huang Jialing; Xu Hao; Li Bingju; Qin Qing; Zhong Chongmao. Preparation method of pharmaceutical intermediate 2,3,4-trimethoxybenzaldehyde. CN200310112817.X, application date 2003-12- 31
[4] Wang Liuwu; Wei Wei; Wei Xiaoting; Wang Suohai. A preparation method of 2,3,4-trimethoxybenzaldehyde. CN201210383432.6, application date 2012-10-11
[5] Technical guidelines for chemical drug impurity research



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
