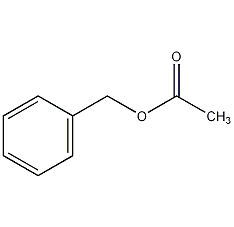
Structural formula
| Business number | 03SR |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C9H10O2 |
| Molecular weight | 150.17 |
| label |
Benzyl acetate, Benzyl acetate, Acetoxytoluene, Benzyl ethanoate, Acetic acid phenylmethyl ester, spices |
Numbering system
CAS number:140-11-4
MDL number:MFCD00008712
EINECS number:205-399-7
RTECS number:AF5075000
BRN number:1908121
PubChem number:24891598
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless liquid with a fragrant jasmine aroma.
2. Density (g/mL, 16/4℃): 1.055
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 5.1
4. Melting point (ºC): -51.3
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 213
6. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.0550
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.5232
8. Flash point (ºC, closed): 102
9. Viscosity (mPa·s, 45ºC) : 0.001399
10. Flash point (ºC): 461
11. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.04432.5
12. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.4995
13. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 10~55ºC): 60.29
14 . Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 19.945
15. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.088×1010
16. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 32.8ºC, constant pressure) : 1.03
17. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 84.150
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: 0.23% dissolved in water. Insoluble in glycerin, but miscible with alcohols, ethers, ketones, aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, etc.
20. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 253.3
Toxicological data
Its vapor can irritate the eyes, skin and mucous membranes, and can cause vomiting, diarrhea and eventually digestive organ disorders after oral administration. The oral LD50 in rats is 2.49~3.69g/kg. Mice exposed to 1.3g/m3 of benzyl acetate for 7 to 13 hours had difficulty breathing and died of anesthesia.
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 43.70
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 125.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 332.0
4. Surface tension (3.0 dyne/cm): 49.7
5. Polarizability (0.5 10-24cm 3): 17.32
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. RotatableNumber of � bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 126
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Benzyl acetate is difficult to dissolve in water and is not easily hydrolyzed. When hydrolyzed with an alkaline alcohol solution in acetone solution, acetic acid and benzyl alcohol are generated. The hydrolysis rate is 10% in 1 hour at 20°C, 35% in 3 hours, and 46% in 5 hours. Using nickel as a catalyst, hydration is carried out at 180°C to obtain toluene and acetic acid. In the presence of sodium ethoxide or sodium methoxide and chloroform, it is heated together with methyl benzoate to generate benzyl benzoate (yield 30%~50%). Benzyl acetate undergoes chlorination reaction at 150~170℃ to generate benzoyl chloride and acetyl chloride. It reacts with bromine at room temperature to form o- or p-bromobenzoyl bromide. When heated to near the boiling point, bromoethane and benzoyl bromide are produced. Benzyl acetate and metallic sodium are heated together, and the product is decomposed with dilute sulfuric acid to produce benzyl hydrocinnamate and dibenzyl ether. Others include cinnamic acid, benzyl acetoacetate, benzyl alcohol, and toluene. Benzyl alcohol can be obtained quantitatively by heating benzyl acetate with absolute ethanol or sodium acetate dehydrated at 160°C.
2.The toxicity of this product is relatively mild, and the oral LD50 in rats is 2490mg/kg. It has stimulating and anesthetic effects. Mice exposed to the concentration of 1.3g/m3 for 7 to 13 hours will have difficulty breathing and die from anesthesia. Due to the low volatility of this product, there are no other adverse effects on humans except local irritation. The operating area should be kept well ventilated. And provide protective equipment for operators.
3. Exists in flue-cured tobacco leaves, burley tobacco leaves, oriental tobacco leaves, and mainstream smoke.
Storage method
1. Keep away from fire sources and strong oxidants, and store in a cool and ventilated place. Iron drum packaging.
2. The equipment must be sealed during the production process and good ventilation should be maintained in the workshop.
Synthesis method
1. Using benzyl alcohol and acetic acid as raw materials, they are directly esterified under the catalysis of sulfuric acid to produce benzyl acetate, which is then neutralized, washed with water and fractionated to obtain the finished product. 
2. Benzyl chloride and sodium acetate are used as raw materials, and benzyl acetate is produced by reacting in the presence of catalysts pyridine and dimethylaniline. The finished product is then washed and distilled. 
3. Tobacco: BU, 14; OR, 57; FC , 9, 18; OR, 18; FC, 40.
4. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, dropping funnel, and reflux condenser, add 60g of powdered anhydrous sodium acetate (0.73mol), glacial acetic acid 100mL. Heat with stirring to dissolve. 63g (0.5mol) of benzyl chloride (2) was slowly added dropwise. After the addition, continue stirring and refluxing for 5 hours. Leave it overnight, filter out the sodium chloride, and then evaporate the acetic acid under reduced pressure. After cooling, add an appropriate amount of cold water, separate the organic layer, wash with water, and dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Distill under reduced pressure and collect the fractions at 90-94°C/1.33kPa to obtain 60g of benzyl acetate (1) with a yield of 80%. [1]
Purpose
1. Spices use. Benzyl acetate is the main component of jasmine and other extracts, and is an indispensable spice in the preparation of floral essences such as ylang ylang. Because of its low price, it is mostly used in soaps and other industrial flavors. It is often used in large amounts in flavors such as jasmine, white orchid, hosta, moonflower and narcissus, and can also be used in small amounts in edible flavors such as raw pears, apples, bananas, and mulberries.
2. Uses in solvents Benzyl acetate dissolves 0.23% (weight) in water and is insoluble in glycerol. But it is miscible with alcohols, ethers, ketones, aliphatic hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, etc. It has good dissolving ability for grease, nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, etc., and can also dissolve rosin, glycerol trirosinate, coumarone resin, etc. Therefore, it is used as a solvent for shellac paint; alkyd resin; nitrocellulose; cellulose acetate; dyes; grease; printing ink, etc.
3.fruit, pineapple, grape, banana, strawberry and other fruity food flavors, the dosage is Normal production needs, generally 760 mg/kg in chewing gum; 34 mg/kg in candy. /span>; 22mg/kg in baked goods; 14mg/kg; 7.8mg/kg in soft drinks.
4. The pure product is used to prepare jasmine type and other floral essences. Commonly used products are used as solvents for resins and are also used in spray paints and inks.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
