Background and overview[1-3]
4-(Chloromethyl)benzaldehyde is an organic intermediate commonly used as raw material for pharmaceutical synthesis. It can be obtained by one-step oxidation of 4-chloromethylbenzyl alcohol.

Preparation[1-3]
Method 1
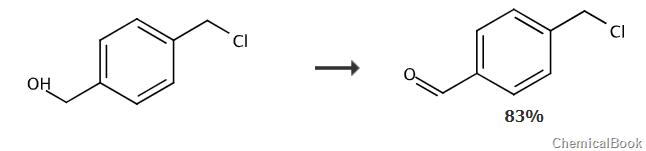
Report 1
Dissolve pyridinium chlorochromate (4.96 g, 23.0 mmol, 1.2 equiv) in 60 mL CH2Cl2, then add 4-chloromethyl Benzyl alcohol (3.00g, 19.2 mmol) was stirred. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours until the starting material disappeared as monitored by TLC (CH2Cl2), and then poured into 200 mL of diethyl ether. The supernatant was removed and the gummy residue was triturated with 200 mL Et2O for 20 minutes. Wash the combined organic solutions with water (3 x 100 mL), 5% NaHCO (2 x 100 mL) and brine (100 mL). Dry with Na2SO4 and remove the solvent under reduced pressure to obtain the crude product as an off-white solid. Purification by flash chromatography (hexane:EA 90:10) afforded 4-(chloromethyl)benzaldehyde as a white crystalline solid (2.79 g, 18.0 mmol, 94%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ9.99 (s, 1H), 7.85 (m, 2H), 7.53 (m, 2H), 4.60 (s ,2H). 13C NMR (75.5 MHz, CDCl3) δ191.46, 143.71, 136.07, 129.95, 128.98, 45.13. EI MS: m / z 154.0 [M] +
Report 2
MnO2 (51.08 g, 587.5 mmol) was added to a solution of [4-(chloromethyl)phenyl]methanol (9.2 g, 58.75 mmol) in DCM (608 mL) middle. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 48 hours. The oxidant was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was concentrated in vacuum to obtain 4-(chloromethyl)benzaldehyde, yield (7.5 g, 83%), as a white solid.
Method 2
Step 1,
Synthesis of 2-(4-formylphenyl)-1,3-dioxolane
Add 400 mL of toluene to 134 g of p-benzaldehyde and 62 g of ethylene glycol, and then add 2 g of p-toluenesulfonic acid to perform a dehydration reaction under azeotropic conditions. After the reaction stopped producing water, the reaction solution was heated under reflux for another 2 hours and then cooled. The resulting reaction solution was poured into aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution. The organic phase was concentrated and then purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain 2-(4-formylphenyl)-1,3-dioxolane, yield 122 g, 68.5%
Step 2,
Synthesis of 2-(4-hydroxymethylphenyl)-1,3-dioxolane
Add 300 mL of water and 500 g of ice to 100 g of 2-(4-formylphenyl)-1,3-dioxolane, and stir. Add sodium borohydride to it little by little. After confirming the disappearance of the raw materials by TLC, the resulting solution was extracted twice with ethyl acetate and dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent is then distilled off. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography to obtain the target compound 2-(4-hydroxymethylphenyl)-1,3-dioxolane, yield 95 g, 93.8%
Step three,
Synthesis of 4-(chloromethyl)benzaldehyde
Add 300 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid to 80 g of 2-(4-hydroxymethylphenyl)-1,3-dioxolane, and then heat the solution to reflux for 24 hours. After the solution cooled, the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration, washed with water, and then dried at room temperature. The resultant was recrystallized from methanol/water to obtain 4-(chloromethyl)benzaldehyde, yield 47 g, 68.4%
Main reference materials
[1] From Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127(25), 9271-9276; 2005
[2] From PCT Int. Appl., 2011143426, 17 Nov 2011
[3] From PCT Int. Appl., 2005092847, 06 Oct 2005



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
