Background and overview[1]
Prostaglandins are an important class of endogenous physiologically active substances. They are important mediators in various physiological processes and have high pharmacological activity. Clinically, prostaglandins are all artificially synthesized. Coreylactonephenylbenzoate, (3aR, 4S, 5R, 6aS)-(-)-hexahydro-4-(hydroxymethyl)-2-oxo-2H-cyclopenta[ b] Furan-5-yl 1,1′-biphenyl-4-carboxylate) is a chiral intermediate for the synthesis of PGF2α prostaglandin drugs. Its molecular formula is C21H20O5 and its chemical name is hexahydro-4-(hydroxymethyl). -2-Oxo-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-5-yl 1,1′-biphenyl-4-carboxylate, usually including (±)biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone, (-)Biphenyl-4-carboxylicolactone and (+)biphenyl-4-carboxylicolactone, reported as 2-oxabicyclo[3.3.0]oct-6-ene-3 -Ketone is used as raw material, and biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone is synthesized through five-step reaction. The main problems of this method are: many steps, complex operations, and long cycle; many process side reactions, difficult to control quality, high product impurities, low purity, and low yield; triphenylmethanol, a by-product produced in the process, cannot be recovered, and it is difficult to dispose of waste. increase cost. These reasons affect the prospects for the use of biphenyl-4-carboxylicolactone, which in turn affects the further development and application of prostaglandin drugs. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a method for preparing biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone with few steps, simple operation, short cycle, high purity, high yield and low cost. The preparation of methanol is very necessary to improve the effective utilization of waste and to develop the application of biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone.
Preparation[1]
A method for producing both trityl alcohol and biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone is to use commercialized colic acid lactone diol dihydroxy derivatives as raw materials, and react in primary hydroxyl groups under acidic conditions. A hydrolysis reaction occurs at the position, the reaction system is neutralized, and then crystallization and recrystallization are performed respectively to prepare triphenylmethanol and the corresponding optically active biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone. The specific steps are as follows:
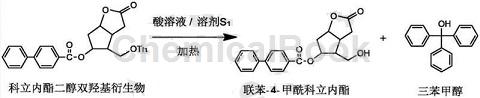
(A) Preparation of the neutralization reaction solution: Add the corylide diol dihydroxy derivative into the solvent S1, add the acid solution while stirring, and control the temperature to 40-60°C for 1-6 hours until the reaction is complete. Cool to room temperature, and solids will precipitate to obtain a hydrolysis reaction solution; add the hydrolysis reaction solution to an alkali solution to neutralize, precipitate solids, and obtain a neutralization reaction solution;
(B) Crystallization: Stir the neutralization reaction solution obtained in step (A) at a temperature of 40-70°C for 1-4 hours until the solid is dissolved, cool to room temperature and leave for 1-5 hours to precipitate the solid to obtain a crystallization liquid ; Filter the crystallization liquid and collect the filter cake to obtain crude trityl alcohol; collect the filtrate of the crystallization liquid, evaporate the solvent S1 under reduced pressure, cool to room temperature and leave it for 1-5 hours to precipitate the solid to obtain an aqueous solution, filter and collect the filter cake to obtain Crude biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone;
(C) Tritylmethanol recrystallization: Add the crude tritylmethanol collected in step (B) into the tritylmethanol recrystallization solvent (dual solvent S2/S3) for reflux reaction for 1-5 hours, and cool to room temperature. Precipitate the solid, filter and wash to obtain pure triphenylmethanol;
(D) Recrystallization of biphenyl-4-formylcolide: add biphenyl-4-formylcolide crude product obtained in step (B) to biphenyl-4-formylcolide Reflux the reaction in the lactone recrystallization solvent (double solvent S4/S5) for 1-5 hours, cool to room temperature, filter and wash the precipitated solid to obtain pure biphenyl-4-carboxylic acid lactone.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201711468377.X A method for preparing triphenylmethanol and biphenyl-4-carboxylicolactone



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
