Overview【1】【2】
4-Aminobenzenesulphonate (4-ABS), commonly known as sulfamate, is an important intermediate widely used in the production of chemical products such as dyes, printing and dyeing auxiliaries, spices, food pigments, medicines and pesticides. , it is also an intermediate product after anaerobic decolorization of many azo dyes. It contains amino (-NH2) and sulfonic acid (-SO3) amphoteric functional groups, giving it unique physical and chemical properties, high polarity, and easy solubility. It is in water and has a stable chemical structure. Wastewater containing sulfonate aromatic amine compounds has the characteristics of high concentration, high color, and high toxicity. It is an organic wastewater that is difficult to biodegrade and can easily cause serious water pollution. Para-aminobenzene sulfonic acid is biologically toxic, and its wastewater is difficult to be treated directly by biochemical methods. At the same time, para-aminobenzene sulfonic acid is stable in nature.
Physical and chemical properties【1】
P-Aminobenzenesulfonic acid is white or off-white crystal. The hydrate loses water at 100℃, and the anhydrous substance begins to decompose and carbonize at 280℃. The relative density is 1.485 (25/4). It is slightly soluble in cold water and insoluble in ethanol. , ether and benzene, are significantly acidic and can be dissolved in caustic soda solution and sodium carbonate solution.
Degradation mechanism【3】
There are two opinions on the degradation mechanism of p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid, which may be related to the characteristics of the degrading strains. Protocatechuic acid is an important intermediate product in the degradation of various aromatic compounds. Its aromatic ring cleavage methods are divided into ortho cleavage and para cleavage. The relevant catalysts are PCA-3, 4, dioxygenase and PCA-4,5 dioxygenase. During the degradation of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid by S1 and S2, sulfonic acid substrates can only induce the production of PCA-3,4 dioxygenase, which follows ortho-cleavage. During the degradation of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid by PNS-1, a yellow ortho-cleavage signature substance was not detected. Whether the intermediate product can be detected depends on the degradation ability of the bacteria. If the strain can completely degrade p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid, it may directly enter the tricarboxylic acid cycle without leaving any intermediate products under the catalysis of the enzyme.
Preparation method【4】【5】【6】
There are two production processes for p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid: solid phase method and liquid phase method. The solid phase method is to bake the reacted aniline sulfate for transposition, and then bake the sulfonic acid group at high temperature to undergo molecular rearrangement and transfer to the para, ortho and meta positions; this method is labor-intensive, and aniline is easily volatile and The char produced by oxidation affects the quality of the product; while the liquid phase method uses a high boiling point organic solvent as a translocation carrier to achieve intramolecular rearrangement of aniline sulfate. The above two methods are currently commonly used industrial methods; but both have high energy consumption. Disadvantages of poor production environment. As a new method of organic synthesis, microwave has the advantages of saving energy, uniform heating, and fast reaction speed, and has become a hot spot in organic synthetic chemistry.
1. Microwave synthesis of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid
Add 5 mL of freshly steamed aniline into a 100 mL round-bottom flask, cool the flask in a cold water bath, add concentrated sulfuric acid in batches under shaking, then place the round-bottom flask in a microwave oven, install a reflux condenser and stir device. Under stirring, first heat with a power of 65 W for 1 min, and then heat the reaction with a certain microwave power and a certain reaction time. After the reaction is completed, take out the round-bottomed flask, wait until the reactant is slightly cold, pour it into a beaker containing 30 mL of cold water while it is hot under stirring, rinse the reaction flask with a little hot water, merge the washing liquid into the beaker, cool and filter with suction. The crude product is recrystallized with water, activated carbon is added for decolorization, and the product is vacuum dried.
2. Preparation of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid by microwave translocation of aniline sulfate
Add 100mL of aniline into a 500mL three-necked round-bottomed flask with stirring, and slowly drip 200-250mL of 95% sulfuric acid from the dropping funnel while stirring. The temperature will naturally rise to 190°C. After the reaction is insulated at this temperature, The reaction material is poured into a porcelain plate; the material is cooled and solidified to obtain aniline sulfate. Put 50g of aniline sulfate sample into the sealed sample melting tank of the WX-3000 microwave rapid digestion instrument, gradually adjust the microwave radiation power and temperature through the display screen of the digestion instrument control panel, and discharge the material after the radiation reaction reaches the specified time. The translocated material is dissolved in 5% sodium hydroxide solution, filtered and a small amount of anhydrous sodium sulfite is added, and the pH=2 is adjusted with sulfuric acid to crystallize p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid.
3. Synthesis of p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid by solvent method
(1) Solvent treatment
The boiling range of solvent gasoline is 160~200℃, and the solvent must be inertized. The specific method is as follows: add an appropriate amount of concentrated sulfuric acid to the solvent, stir it to fully contact it, and after a certain period of time, pour it into a separatory funnel, let it stand for layering, release the waste liquid, and wash the treated solvent with water until it is neutral. Take a certain amount of solvent, add an appropriate amount of 0.05% potassium permanganate aqueous solution, shake it thoroughly, let it stand for layering, release the potassium permanganate solution and compare the color with the original solution. If the depth of the solution does not change, it proves that the treated solution contains A small amount of unsaturated hydrocarbons have been removed and the solvent is inert.
(2) Experimental operation
Add 60 mL solvent gasoline and 0.1 mol aniline into a four-neck bottle equipped with a stirrer, dropping funnel, condenser and thermometer, and slowly drop concentrated sulfuric acid under stirring to form a salt. After the dripping is completed, after the salt is completely formed, the temperature is slowly raised to 170~175°C and maintained for 6 hours to carry out dehydration translocation reaction. During the reaction, the solvent is continuously dripped in and the solvent is continuously evaporated, keeping the total solvent amount in the reactor basically unchanged. After the reaction is completed, cool down, pour out the solvent, add water, and add a small amount of anhydrous sodium sulfite. After it is dissolved, use Na2CO3 solution to adjust pH = 7 to 8, filter, discard the filter residue, add a small amount of anhydrous sodium sulfite to the filtrate, and use dilute Acidify with sulfuric acid to pH=2. After filtering, washing and drying, the product is obtained. Product pureDegree > 98%.
Production process【7】
1. Process:
In a 1000 liter jacketed sulfonation pot with a stirring device. First, put in 214 kilograms of sulfuric acid divided into 100 solutions, start stirring, and slowly drop 200 kilograms of aniline into 100 solutions into the sulfonation pot. And use the aniline dripping speed to control the temperature in the pot at 155-160°C. After the dripping is completed in about two hours, gradually pass the organic heat carrier heating agent-biphenyl mixture vapor into the sulfonation pot jacket. At this time, start During the heating operation, when the temperature of the reaction materials in the pot rises to 205°C, the temperature rise is stopped, and the temperature is maintained for a period of time while stirring. As the water content of the materials continues to escape, the temperature in the pot can reach 215°C. When the temperature shows no upward trend, it is determined After the sulfonation reaction is completed, the powdered p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid after natural cooling is vacuum-evacuated to the storage bin.
2. Process conditions:
The reaction formula of sulfonation of aniline and concentrated sulfuric acid is:
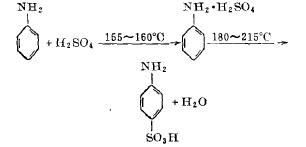
Figure 1 is the sulfonation reaction formula of aniline and concentrated sulfuric acid
(1) Ingredient ratio
The sulfonation of aniline and sulfuric acid is an equimolecular reaction. In order to make the reaction complete and aniline is expensive, aniline: sulfuric acid = 1:1.015 kg per molecule. The amount of sulfuric acid used is small. The reaction of aniline will be incomplete and the consumption will increase; the use of large amounts of sulfuric acid will increase the inorganic acid content in p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid, which will not only corrode equipment and pipelines, but also consume a large amount of soda ash during neutralization in the next process, causing undue stress. There is some waste and loss, and at the same time, it is easy to cause accidents of cans and materials.
(2) Reaction temperature
The reaction of sulfonation of aniline and sulfuric acid to form p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid is carried out in two stages. The first is the salt-forming reaction, which is a strong exothermic reaction; the second is the sulfonation translocation reaction, which is an endothermic reaction. If you want to carry out the above two reactions in the same equipment, the temperature control is The key point is that in order to complete the salt-forming reaction, the salt-forming temperature is controlled by dropping aniline at a rate of 155-160°C. The translocation of aniline sulfate will only occur when it is above 150°C, so the temperature between salt formation and transposition is The difference is the heating time after salt formation. However, the transposition temperature should not be too high. The final material temperature is limited to 215°C. If it is too high, the material will be carbonized and the content will be reduced.
(3)Reaction time
The appropriate salt-forming reaction time from the dropwise addition of aniline to the beginning of translocation is 2.5-3 hours. The most appropriate time for the translocation reaction is 3-4 hours depending on the heat source supply.
(4) Stirring form and speed
The sulfonation reaction of aniline and sulfuric acid is divided into two stages: salt formation and transposition. Salt formation is a liquid reaction, while during the transposition reaction, the material changes from liquid to solid. The above two reactions must be carried out in the same When carried out in equipment, it is necessary to consider not only sufficient stirring during the liquid reaction, but also the resistance to stirring after forming a solid state, and the preparation of powdered materials. In order to make the two reactions complete, the form, speed, power, etc. of the mixing device must be reasonably selected. Our factory uses strong bevel gear reduction, paddle-type and anchor-type combined mixers, and the mixing speed is 57 rpm. ;The motor power is 10 watts.
(5) Transposition heating
The translocation of aniline sulfate is an endothermic reaction. A biphenyl mixture is used as the heating agent. The heating form is gas phase forced circulation. The maximum pressure of the biphenyl mixture steam boiler is controlled above 1 kg/cm2.
(6) Pneumatic discharging
Powdered p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid is transported by pneumatic, and the discharging method is vacuum pumped to the storage bin for use in the next process.
Purpose【3】
1. As a typical representative of sulfonic acid aromatic compounds, p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid has a wide range of uses and is an important dye intermediate. It can be used to produce acid orange II, acid bright yellow 2G, and acid medium yellow brown 4G. , acidic medium dark yellow GG, direct yellow GR, reactive yellow K-RN, brilliant red K-10B, brilliant red K-2G, jujube K-DG and purple K-3R, etc. can also be used to make printing and dyeing auxiliaries, such as dissolved salts B. Optical brightener BG, optical brightener BBU, anti-stain salt H, etc. are also ideal raw material intermediates for spices, food pigments, pharmaceutical and building materials and other industries.
2. A pesticide that can be used to prevent wheat rust and has a systemic therapeutic effect on wheat rust is called sodium dichloride.
Main reference materials
[1]Huang Peiyu. Experimental study on pretreatment of high-concentration aniline and p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid wastewater by emulsion liquid film method[D]. Chongqing University, 2011.
[2]Wang Yanqing, Zhang Jinsong, Zhou Jihui, Hou Yulin, Zhou Mi, Li Junfang. Study on the biodegradation kinetics and degradation mechanism of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid [J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(07): 2136-2141 .
[3]Wang Yanqing. Study on the degradation characteristics of p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid by Pannonibacter sp. W1[D]. Dalian University of Technology, 2009.
[4] Chen Nianyou, Zhao Shengfang, Wu Ziqing. Microwave synthesis of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid [J]. Chemistry World, 2004(08):428-429+406.
[5]Zhang Zhengkai, Shen Liangsu. Preparation of p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid by microwave translocation of aniline sulfate[J]. Sichuan Chemical Industry, 2005(04):4-5.
[6]Su Yanxi, Yang Jiqing. Research on the synthesis of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid by solvent method [J]. Hebei Chemical Industry, 2000(04):12-13.
[7] Zhang Xueyu, Wang Shuping. New process of p-aminobenzene sulfonic acid [J]. Pesticide Industry, 1975(02):33+42.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
