Background and overview[1][2]
4-Chloroaniline (4-chloroaniline 4-chloroaniline) is a white or yellow crystal with a melting point of 341~344K and a boiling point of 505K. It is easily soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone and carbon disulfide. 4-Chloroaniline 4-Chloroaniline is an important raw material in fine chemical production and is widely used in the fields of synthetic medicine, pesticides, rubber and daily chemicals. Its demand is increasing with the development of the chemical industry. At present, most 4-chloroaniline is produced by the reduction of p-chloronitrobenzene. The main reduction methods include metal reduction, electrochemical reduction, non-hydrogen reducing agent reduction, catalytic hydrogenation reduction, etc. Among them, catalytic addition The hydrogen reduction method has advanced technology and high yield, which is more in line with the requirements of modern chemical industry for atom economy; among them, the precious metal catalytic hydrogenation method occupies a dominant position. In the past, the heterogeneous catalytic reduction method under high temperature and high pressure was mainly used. However, due to the microcrystalline at high temperature, It is easy to aggregate on the surface of the carrier, affecting its dispersion and thus affecting the catalytic activity of the catalyst. In recent years, heterogeneous catalysis at low temperature and low pressure has gradually attracted the interest of scientific researchers. The key point of the catalytic hydrogenation method is how to control the selectivity of the reaction and prevent the occurrence of dechlorination side reactions.
Apply[3]
4-Chloroaniline is an important raw material in fine chemical production and is widely used in the fields of synthetic medicine, pesticides, rubber and daily chemicals. Its demand is increasing with the development of the chemical industry. For example, in the dye industry, 4-chloroaniline is an important intermediate for the synthesis of dyes and phenol AS-LB; in the pharmaceutical industry, 4-chloroaniline is an important intermediate for the synthesis of phenadine and chlordiazepoxide. Intermediates for other drugs; in addition, 4-chloroaniline 4-chloroaniline can also be used to produce bactericides, polyurethane resin cross-linking agents and color film couplers.
Preparation [2-3]
1. Metal powder reduction
The iron powder reduction method is the earliest method used to reduce nitro compounds, and it is also a widely used reduction method. Under certain conditions, metals whose electromotive force ranks before hydrogen can be used to reduce p-CNB and hydrogenate to prepare 4-chloroaniline 4-chloroaniline, such as K, Ca, Al, Zn, Fe, etc. Among all metals, considering the cost issue, iron powder is the most commonly used metal. Its reaction formula for reducing p-CNB in acidic medium is as follows:
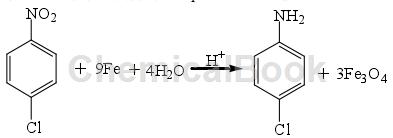
This method is easy to operate, has good product selectivity, and the process is relatively mature; however, acidic conditions require higher equipment, and the discharge of acid-containing wastewater and waste residue will cause serious pollution to the environment. To overcome the above shortcomings, researchers have discovered several reducing agents that can replace Fe powder. Using Al powder as a reducing agent in an acidic medium HCl aqueous solution can reduce o-, m-, and p-bronitrobenzene to o-, m-, and p-bromoaniline. The oxidation product of Al powder is Al2O3. Zn powder was used as a reducing agent to reduce 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene to prepare 2-fluoro-5-nitroaniline. It was found that when the amount of Zn powder was 4 times the amount of the reactant, in ethanol as Solvent, reaction temperature was 323-333K for 3 hours, and the yield of the product 2-fluoro-5-nitroaniline was 70.1%.
2. Alkali sulfide reduction method
The alkali sulfide reduction method is suitable for the catalytic hydrogenation reaction of nitro compounds containing groups that easily react with acids, using Na2S, Na SH and Na2S2 (sometimes also using H2S or Fe S) as reducing agents, in
Method of reducing nitro compounds in the presence of H2O. Taking the reduction of p-CNB with Na2S2 as an example, the reaction formula is as follows:
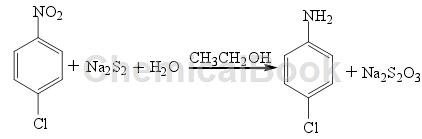
In a weakly alkaline environment, under the condition of hydrogen pressure of 100-200k Pa, use H2S as a reducing agent to reduce halogenated nitrobenzene to prepare the corresponding halogenated aniline. Using Na2S2 as the reducing agent to reduce p-chloro-o-nitrophenol, the yield of the product p-chloro-o-aminophenol was 72%. Since alkali sulfide is a weak acid and strong alkali salt, only nitro compounds that react in an alkaline medium can be reduced using this method. This method is similar to the iron powder reduction method
It has the advantages of mild experimental conditions, easy separation of reducing agent and reaction products, and less corrosion to the reactor;
However, the price of sulfide alkali is high, the product yield is not high, and a large amount of waste liquid is still produced during the reaction, which pollutes the environment.
3. Hydrazine hydrate reduction method
The reduction method of hydrazine hydrate (N2H4) is a relatively commonly used reduction method. The reduction of halogenated nitrobenzene by N2H4 is a relatively special process, that is, N2H4 will decompose hydrogen during the catalytic reaction. N2H4 itself does not have the ability to reduce Performance, but in the presence of a catalyst, halogenated nitrobenzene can be reduced to the corresponding halogenated aniline. The reaction equation is as follows:
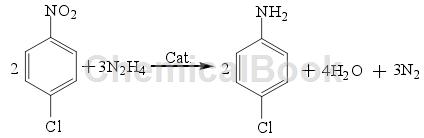
N2H4 will decompose into hydrogen only in the presence of a cocatalyst. Therefore, the reaction can be carried out under low temperature and low pressure conditions, and has good product selectivity; however, N2H4 itself has shortcomings such as highly toxic, expensive, and difficult to store, which greatly limits its industrial application.
4. Electrochemical reduction method
4-Chloroaniline 4-chloroaniline can also be prepared from p-CNB by electrochemical reduction. Direct electroreduction and indirect electroreduction are two commonly used electrochemical reduction methods. In the direct reduction method, the reducing substances are electrons; in the indirect reduction method, the reducing substances are electrons.The reaction formula of 4-chloroaniline is as follows:
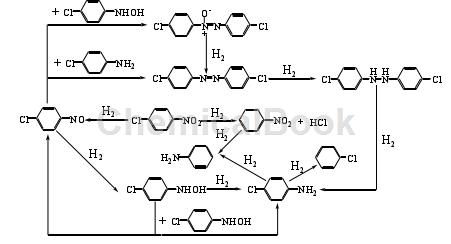
At present, there are two main methods that can effectively inhibit the hydrodechlorination of p-CNB: one is to add dechlorination inhibitors to the reaction system, such as morpholine, organic amines with p Kb<3, thiophene, etc.; Hydrodehalogenation can be avoided as much as possible by selecting appropriate processes. Poisoning or modifying the catalyst can also inhibit dehalogenation. Dechlorination inhibitors mainly achieve the purpose of inhibiting the hydrodechlorination of p-CNB by changing the electronic structure of the metal on the catalyst surface. Under the condition of using skeleton Ni and 5% Pd/C as catalyst, adding thiophene as dechlorination inhibitor in the reaction system, using methanol as solvent to reduce several dichloronitrobenzene, and under suitable temperature and pressure conditions, the system was prepared. The selectivity of the corresponding dichloroaniline was as high as 99%. Ni is used as a catalyst to catalyze the hydrogenation of p-CNB, and the dechlorination inhibitor is (CNE). Under the conditions of temperature and pressure of 333K and 0.6MPa respectively, after 165 minutes of reaction, the selectivity of the product 4-chloroaniline 4-chloroaniline is 99.2%. Although adding dechlorination inhibitors can improve the selectivity of the product, it will also reduce the catalytic reaction activity. The nature and dosage of the dechlorination inhibitors have a great impact on the selectivity of the target product. Moreover, the addition of dechlorination inhibitors makes it more difficult to separate the target product from the reaction system.
Main reference materials
[1] Study on selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene to 4-chloroaniline using mesoporous TiO_2 supported Pt_Fe_catalyzed_omitted_chloronitrobenzene
[2] Preparation method of 4-chloroaniline
[3] CN201711340016.7 A method for preparing 4-chloroaniline by selective hydrogenation of p-chloronitrobenzene



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
