Background and overview[1][2]
Trimethylbenzene is a colorless, flammable and volatile liquid. Molecular weight 120.19. There are three isomers, namely mesitylene, mesitylene and mesitylene. Their physical and chemical properties are slightly different. They are insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol, ether and benzene. Mainly used as chemical raw materials, solvents and paint thinners, it is slightly toxic. It can be slowly absorbed through the digestive tract, respiratory tract and skin. Oxidized in the body to phenolic and formic acid compounds.
The former combines with sulfate radicals and a small amount with glucuronic acid radicals. The latter is mainly combined with glycine and excreted in the urine; a small amount is excreted unchanged through the lungs or kidneys. There have been no reports of occupational poisoning. When the concentration of this product mixture in the workshop air is 50 mg ~ 300 mg/m3, workers often have symptoms such as weakness, headache, dizziness, or reduced numbers of platelets and red blood cells, gum and nose bleeding, subcutaneous hematoma, etc. Asthmatic bronchitis may still be seen in those exposed to higher concentrations. Acute poisoning patients may experience symptoms such as central nervous system depression or loss of reflexes.
Structure
The structures of mesitylene, mesitylene and trithionine from left to right are:
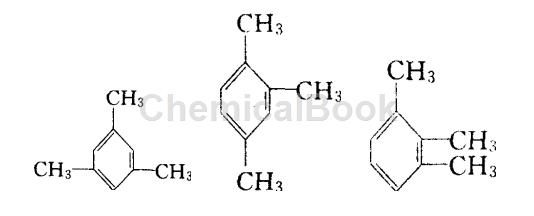
Preparation[2-4]
1. Trithionine: A method of purifying trithionine from mixed C9 aromatic solvent oil, that is, using alkylation and dealkylation to mix C9 A method for producing high-purity trithionine with a purity of more than 92% by using aromatic hydrocarbon solvent oil as raw material through the processes of alkylation, distillation, dealkylation and re-distillation. The specific methods are as follows:
1) Place the mixed C9 aromatic hydrocarbon solvent oil in the reactor, raise the temperature to 40~140°C, add the catalyst anhydrous aluminum trichloride, and mix the catalyst and mixed C9 The mass ratio of aromatic hydrocarbon solvent oil is 0.1: 10~1.5:10, stir evenly;
2) Pour in the alkylating agent C2~C5 olefin under constant stirring to carry out the alkylation reaction, and remove the trithionine in the raw material. Alkylation into alkyl mesitylene, the molar ratio of the amount of alkylating agent to mesitylene in the raw material is 1:1~3:1, the temperature is controlled at 40~140℃ during the entire alkylation reaction. After the alkylating agent is introduced, continue stirring for 10 to 60 minutes to make the alkylation reaction more complete;
3) Wash the alkylation liquid with water at 40 to 140°C and let it stand still. Take the upper alkylation liquid and carry out vacuum distillation of the alkylation liquid in the alkylation liquid distillation tower. The vacuum degree is When it is 600~745mmHg, cut out the alkyltrimethylbenzene fraction;
4) The alkyltrimethylbenzene fraction cut by distillation is subjected to a dealkylation reaction under the action of the catalyst M-H molecular sieve. The catalyst M-H molecular sieve is one or more of Co ions, Ce ions, Ag ions, Ni ions, and Pd ions. The seed salt is exchanged with X-type molecular sieve or Y-type molecular sieve according to 0.001-0.01mol/g, and the reaction temperature is 300~650℃;
5) Carry out vacuum distillation or normal pressure distillation of the dealkylation liquid under a vacuum of 600-745 mmHg to obtain high-purity mesitylene.
2. Mesitylene: A method of producing mesitylene from xylene, mesitylene, and tetramethylbenzene.
This method has a conversion rate of 75 to 85% of the raw material trimene, high yield of the target product, and low preparation cost. Using xylene, mesitylene, and tetramethylbenzene as raw materials and anhydrous aluminum trichloride as the catalyst, an isomerization reaction is performed under normal pressure to obtain a reaction solution containing mesitylene products that is washed with water and alkali and then sent to The rectification tower separates the mesitylene product with a purity of 98.5%.
In addition, methyl chloride is added to the recycled dimethylbenzene and tetramethylbenzene for alkylation reaction, and the reaction liquid containing the mesitylene reaction product is obtained. After washing with water and alkali, it is sent to the distillation tower for separation to obtain homogeneous mesitylene with a purity of 98.5%. Trimethylbenzene product, characterized in that: the feeding ratio of xylene, trimylene and tetramethylbenzene is 1:2.5~3:1~1.5; the isomerization reaction temperature is 100~120℃, and the reaction time is 3~8 hours , the amount of catalyst added is 2~7%; the alkylation reaction temperature is 120~130℃, the reaction time is 3~4 hours, and the amount of alkylating agent added is 30~60m3/ m3·h.
3. Trimethylbenzene: A method of methylating BTX aromatic hydrocarbons to synthesize trimethylbenzene. This method uses BTX aromatic hydrocarbons (selected from benzene, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene, p-xylene and mixed xylene). One or several compositions) and methylating agent (selected from methanol, dimethyl(one or more of � and methyl chloride) are used as raw materials, and trimethylbenzene is obtained through a methylation reaction catalyzed by an acid catalyst.
The acid catalyst is selected from one of halide, liquid acid, complex acid, heteropoly acid, solid superacid, acidic ion exchange resin, acidic oxide, hydrogen zeolite molecular sieve or supported acid catalyst. The methylation reaction pressure is 0.01~10.0MPa, the temperature is 30~700℃, the raw material liquid mass space velocity is 0.1~10.0h-1, and the molar ratio of aromatic hydrocarbons to methylating agent is 1:10~10:1. The methylation reaction can be a fixed-bed continuous reaction or a kettle-type continuous reaction. This method has abundant sources of raw materials, low cost, mild reaction conditions, high single-pass conversion rate of raw materials and high yield of mesitylene.
Purpose[5-7]
1) Trimethylbenzene (1, 2, 4-trimethylbenzene): It is an important organic chemical raw material, mainly derived from catalytic reforming of heavy aromatic hydrocarbons. Trimethylbenzene, as a basic organic chemical raw material, is widely used and has many downstream products with high added value. The main uses of trimellitene are as follows: synthesis of trimellitic acid and trimellitic anhydride; production of mesitylene by isomerization; production of mesitylene by disproportionation and isomerization; synthetic fiber 2, 3, 5-trimethylhydroquinone.
Among them, the synthesis of trimellitic anhydride from trimellitic anhydride has become the main use of trimellitic anhydride. The demand for trimellitic anhydride at home and abroad is growing at a rate of 20%. Since the synthesis of trimellitic anhydride requires high purity of trimellitic acid (the purity is generally required to be above 98.5%, now China basically imports trimellitic acid to produce trimellitic anhydride), so the production of trimellitic anhydride with high purity is of great significance to the further production of trimellitic anhydride.
2) Mesitylene: It is an important fine chemical raw material and has a wide range of applications in production practice. Antioxidant 330, produced with mesitylene as raw material, is stable at high temperatures, has a high melting point and is difficult to volatilize. At the same time, it can maintain the good color of the product and extend its service life. Its performance is better than other commonly used antioxidants. In addition, mesitylene is also a necessary raw material for the preparation of unsaturated polyester and modified fiber. Chemical products such as trimesic acid and trimesic anhydride are also produced by reaction with mesitylene as raw material.
3) Trithionine: As an important intermediate in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, it is widely used in the production of aniline dyes, tertiary acid, synthesis of Tibetan musk, and preparation of platelet anticoagulants and other drugs. For example, using trithionine as raw material to efficiently synthesize Tibetan musk, first, 5-tert-butyl trithionine is generated through a pay-gram alkylation reaction of trithionine, and then reacted with nitric acid under the catalysis of Lewis acid to produce Tibetan musk. After the reaction mixture is diluted, neutralized and filtered through subsequent processing, the pure product is isolated by recrystallization.
The synthesis method of the present invention is simple and efficient, has low raw material requirements, and does not require ultra-high purity trithionine; the reaction conditions require low, and high-purity Tibetan musk can be obtained through simple subsequent processing steps; in addition, The method of the present invention also has much lower environmental pollution than the prior art.
Main reference materials
[1] Health Dictionary
[2] CN200610047287.9 Method for purifying trimethylbenzene from mixed C9 aromatic hydrocarbon solvent oil
[3] CN01120273.4 Method for producing mesitylene from xylene, trimylene and tetramethylbenzene
[3] CN200910195550.2 A method for synthesizing trimethylenene by methylation of BTX aromatic hydrocarbons
[4] CN200410021117.4 Process method for separating trimethylbenzene
[5]CN200510122233.X A method for producing high-purity mesitylene by joint alkylation of propylene and isobutylene
[6]CN201310652640.6 A kind of synthesis method of Tibetan musk



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
