Background and overview[1][2]
Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is a broad-spectrum crop pathogenic fungi inhibitor produced by Jiaotong University through biological fermentation. It is an active ingredient in pesticide preparations against fruits, vegetables and crop diseases and insect pests, and is active in pesticide preparations against rice sheath blight. Element. Such substances can broadly inhibit various crop pathogenic fungi, such as cucumber and watermelon fusarium wilt, melon vine blight, rice sheath blight, pepper root rot and other diseases.
It has been reported that phenazine-1-carboxylic acid can be prepared from 3-nitroaniline through acetyl protection, nitration, deprotection, diazotization, cyanation, coupling with aniline, ring closure, and cyano hydrolysis. This method has long reaction steps, low nitrification selectivity, and requires the use of highly toxic sodium cyanide. It has also been reported that the biopesticide “shenzinmycin” developed by biological fermentation method has phenazine-1-carboxylic acid as its main component.
On the one hand, the preparation of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid by biological fermentation faces problems such as large equipment investment, low production efficiency, and high cost. In addition, the existing synthesis methods have problems such as difficult to obtain raw materials, too long reaction steps, selectivity, and yield. Low-level problems; therefore, seeking an efficient synthesis route has become a technical problem to be solved by the present invention.
2-Bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid, white to yellow powder or crystal, can be used as an intermediate in the synthesis of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. It has been reported that it is synthesized from aniline and 2-bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid. Substituted diphenylamine is obtained through Jourdan-Ullmann reaction, and then the ring is closed to obtain phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. The raw material used in this method, 2-bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid, is expensive and difficult to obtain.
Apply[1]
2-Bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid can be used as a pharmaceutical intermediate, such as the preparation of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. The natural product phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (PCA) is an important microbial metabolite in Pseudomonas (Pseudomonads) and Streptomycetes (Streptomycetes) are widely present in the secretions of microorganisms, and have medical anti-lung cancer activity and resistance to rice sheath blight and watermelon The broad-spectrum agricultural antibacterial activity of pathogenic bacteria such as Fusarium wilt, pepper blight, wheat total rot, watermelon anthracnose and rapeseed sclerotinia is harmless to humans, animals and the environment, and has a unique chemical structure, making it an ideal compound for the development of green pesticides. .
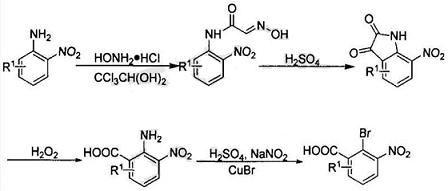
Some research has developed a method for preparing phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, using the following steps: aniline reacts with chloral hydrate and hydroxylamine to produce α-oxime acetanilide, and then treated with concentrated sulfuric acid to obtain isatin, indigo Red reacts with hydrogen peroxide to obtain 2-amino-3-nitrobenzoic acid, and then undergoes Sandmeyer reaction to obtain 2-bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid; the prepared 2-bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid and aniline undergo Jourdan-Ullmann reaction Obtain substituted diphenylamine, and then close the ring to prepare phenazine-1-carboxylic acid.
The α-oximeacetanilide is prepared by the following steps: mix chloral hydrate, hydroxylamine hydrochloride and anhydrous sodium sulfate in a weight ratio of 20-30:60-80:20-30 and dissolve in water , heated to 65°C, add the suspension of 2-nitroaniline to it, the weight ratio of 2-nitroaniline to chloral hydrate is 20-30:20-30, keep the reaction for 20h and then cool to 5-8°C , incubate for 2h, filter to obtain a yellow solid, which is α-oxime acetanilide. The prepared α-oximeacetanilide is mixed with concentrated sulfuric acid in a mass ratio of 20-30:120-140, heated to 90°C for 2 hours, and the reaction solution obtained is placed in ice water, and the temperature is controlled at 5°C to quench the reaction for 2 hours. , prepare isatin.
Add sodium hydroxide solution dropwise to the prepared isatin and stir, cool to 2°C in an ice water bath, add 30wt% hydrogen peroxide dropwise, the mass ratio of isatin to hydrogen peroxide is 20-30:7-10, control The temperature should not exceed 8°C. After the dropwise addition, naturally raise the temperature to 20°C, stir for 15 hours, adjust the pH of the filtrate to 2 after filtration, and then extract with ethyl acetate to obtain 2-amino-3-nitrobenzoic acid.
The phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is prepared by the following steps: a. Stir and dissolve 2-bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid in DMF, then add potassium carbonate and aniline, 2-bromo-3 -The mass ratio of nitrobenzoic acid, potassium carbonate and aniline is 80-100:250-260:80-100, heat to 90℃, keep the reaction for 6-18h, evaporate DMF under reduced pressure, add water and extract once with chloroform . Adjust the pH value of the water phase to 3, keep the precipitated product at 5°C for 2 hours, filter and dry to obtain 2-anilino 3-nitrobenzoic acid; b. ethanol (200g) to 2-anilino 3-nitrobenzoic acid Add sodium borohydride to the solution and heat it to reflux. After refluxing for 2 hours, add sodium borohydride and repeat the reaction until refluxing for 20 hours to recover ethanol.
Add water and activated carbon to reflux and decolorize. After filtration, the pH value of the filtrate was adjusted to 2, and the precipitated solid was kept at 5°C for 2 hours. After filtration and drying, it was recrystallized to prepare phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. As a preferred embodiment, in step a, aniline can also be added during the insulation reaction. The prepared phenazine-1-carboxylic acid can also be derivatized to obtain phenazine-1-carboxylic acid derivatives.
Preparation [1]
2-Bromo-3nitrobenzoic acid is prepared by the following method:
a. Cool the concentrated sulfuric acid to 15°C in an ice water bath, add nitrous acid in several batches, the mass ratio of concentrated sulfuric acid to nitrous acid is 700-750:50-60, and control the temperature not to exceed 35°C when adding nitrous acid , then heated to 70°C to dissolve all the solids, then cooled to 8°C, added glacial acetic acid solution of 2-amino-3-nitrobenzoic acid, the mass ratio of concentrated sulfuric acid to 2-amino-3-nitrobenzoic acid The ratio is 700-750:100, and the temperature is controlled not to exceed 18°C. After the addition is completed, the temperature is raised to 40°C and kept for 2 hours to form a diazonium salt;
b. Mix cuprous bromide with 40wt�The hydrobromic acid solution of � has a mass ratio of 150-180:1200-1300 and is cooled to 4°C in an ice water bath. Add the diazonium salt prepared in step a. When adding the diazonium salt, control the temperature to not exceed 10°C and then remove the ice. Water bath, stir for 1 hour, then heat to 70-80°C, keep the reaction for 2 hours, pour the reaction solution into ice water, precipitate the product, keep it at 5°C for 2 hours, filter and dry to obtain 2-bromo-3-nitrobenzoic acid.
 (R1=H)
(R1=H)
Main reference materials
[1] CN201410045805.8 A method for preparing phenazine-1-carboxylic acid
[2] Wu Qinglai, Xu Zhihong, Li Junkai. Research progress on the synthesis of phenazine-1-carboxylic acid and its analogs[J]. Journal of Pesticides, 2016, 18(6): 669-675.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
