Background and overview[1][2]
1,4-Diiodobenzene is an important organic intermediate that reacts with different reactive groups to synthesize a variety of substituted functional compounds. It is widely used in the fields of medicine, pesticides and materials. Its synthesis and application are extremely research value.
Preparation[1]
There are many methods for synthesizing 1,4-diiodobenzene, among which the diazo-iodination method of aromatic amines is a common method. These methods are mainly divided into the following categories.
P-phenylenediamine hydrochloride is diazotized, and then undergoes a displacement reaction with potassium iodide. The amino group of diphenylamine is replaced by iodine to obtain 1,4-diiodobenzene. Since the raw material p-phenylenediamine has been diazotized twice, the diazotization yield is low; in addition, the content of 4-chlorobenzene iodide and benzene iodide in the product is very high, making it difficult to separate.
In order to simplify the reaction steps, chemists used diazotization of p-iodoaniline and then performed a displacement reaction with potassium iodide to obtain the product 1,4-diiodobenzene. Since the source of p-iodoaniline is scarce, it is difficult to preserve and the price is high, it is difficult to apply it on a large scale in industry.
At present, 1,4-diiodobenzene is usually produced by electrophilic substitution of the benzene ring with iodination in a weakly alkaline sodium bicarbonate medium. After sodium nitrite and acetic acid are used as diazotization reagents, iodination Cuprous and hydriodic acid serve as displacement reagents. Since the freezing point of acetic acid is 16.6°C, it is easy to solidify during low-temperature diazotization, resulting in insufficient reaction. In addition, the prices of copper iodide and hydriodic acid are relatively high, and the dosage of hydriodic acid is large, making the reaction cost high.
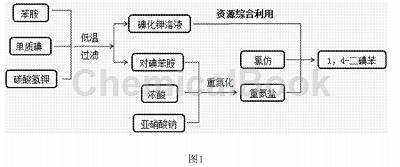
CN201610129881.6 provides a low-cost, green and environmentally friendly preparation method of 1, 4-diiodobenzene. The raw materials of this method are easily available, the yield is high, and it is suitable for industrial-scale production. As shown in the process flow in Figure 1, add 9.3g aniline (0.1mol) to 110ml of 10% (w/w) potassium bicarbonate solution, and then add the molar ratio of crushed iodine to aniline in batches within 15 to 20 minutes. 26.7g of elemental iodine at 1.05:1 was subjected to electrophilic substitution reaction at 5 to 10°C for 4 hours, and filtered after the reaction was completed. The liquid is the potassium iodide solution generated by the reaction, which is directly used in the iodine replacement reaction. After drying the solid, 21.0 g of p-iodoaniline was obtained, with a yield of 95.8%.
HNMR analysis results: 1HNMR (CDCl3, 270MHz), 7.40(d,2H), 6.47(d ,2H), 3.38(s,2H), NMR test shows that it is the target product. Add 21.0g of p-iodoaniline (0.096mol) to 400 ml of water, control the reaction temperature to be less than 0°C, add 90 ml of 36.5% (w/w) concentrated hydrochloric acid with a molar ratio of hydrochloric acid to p-iodoaniline of 11.1:1, and cool quickly. Ultra-fine white crystals precipitate at -10°C, and then 33 ml of 20% (w/w) sodium nitrite solution with a molar ratio of sodium nitrite to p-iodoaniline is 1.15:1 is added dropwise within 15 to 20 minutes. React at -5°C for 4 hours to prepare diazonium salt. The excess sodium nitrite is quenched with a small amount of urea; maintain the reaction temperature at -10°C, add 150 ml of chloroform to the diazonium salt solution prepared above, and then Add 110 ml of recovered potassium iodide solution, react at low temperature for 4 hours, slowly rise to room temperature, and react for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was separated into layers, and the organic phase was washed with sodium sulfite solution until orange, then washed with sodium carbonate solution and water respectively, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and chloroform was recovered by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain 28.39g of light yellow solid. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum analysis results: 1HNMR (CDCl3, 270MHz), 7.45 (d, 2H), the nuclear magnetic resonance test shows that it is the target product. The synthesis method has a molar yield of 80.0% based on aniline, a purity of 93%, and a melting point of 127 to 133°C.
Apply [2]
1. Used to prepare hydrophobic porous materials with nanocavity structure
Hydrophobic materials are functional materials widely used in daily life and industry. CN201810020104.7 provides a hydrophobic porous material with a large specific surface area and nanocavity structures of different sizes, and provides a preparation method and application for the material. The nanocavity structure hydrophobic porous material uses nanosilica as a hard template, and 1,3,5-phenylacetylene and 1,4-diiodobenzene are coated on the surface of the nanosilica through Sonogashira coupling reaction, and then The nano-silica is removed by etching with hydrofluoric acid to obtain a nano-cavity structure hydrophobic porous material, wherein the particle size of the nano-silica is 100 to 500 nm. Nanocavity of the present inventionThe structurally hydrophobic porous material has ultra-high adsorption performance and selectivity for hydroxymethylfurfural. Through the batch kettle adsorption and desorption process, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural can be effectively adsorbed and separated from the fructose dehydration system at room temperature. It has the advantages of simple operation, low energy consumption and environmental friendliness, and is suitable for the field of oil-water separation in various organic wastewater and crude oil leaks.
2. Used in the preparation of phenylbistriazole compounds
1-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole (phenylbistriazole compound) is available As an anti-rust agent, it is used to prevent rust on metal by spraying, soaking, and brushing, so that it can be adsorbed on the metal surface to form a very thin film, which closely adheres to the metal surface and protects copper and other metals from the atmosphere and Corrosion from harmful media and prevention of deeper corrosion.
CN201310055202.1 uses 1,4-diiodobenzene, 1H-1,2,4-triazole, potassium carbonate and copper iodide as the main raw materials, and N,N-dimethylmethane is used in the reaction. When amide (DMF) is used as the solvent and the temperature is controlled at 80-200°C, 1-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1H- can be obtained in high yield. 1,2,4-Triazole and its single crystal. The advantages and features are:
(1) The reaction operation is simple and easy.
(2) The reaction yield is high and the purity of the obtained product is high.
(3) 1-[4-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazole prepared by the present invention can be used Based on dyes and luminescent agents, its production cost is low and its profit margin is large, making it more suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201610129881.6 A green preparation process of 1,4-diiodobenzene
[2] CN201810020104.7 Nanocavity structure hydrophobic porous material and preparation method and application of adsorption and separation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural
[3] CN201310055202.1 Phenyl bistriazole compound and its preparation method and application



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
