Background and overview[1][2]
Benfuracarb is also called benfuracarb. Molecular formula C20H30N2O5S, chemical name N-[2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethylbenzene Furan-7-yloxycarbonyl(methyl)aminothio]-N-isopropyl-β-alanine ethyl ester, reddish brown viscous liquid, vapor pressure 26.7μPa (20℃), relative density 1.171, Flash point (closed type) 114℃. The solubility in water is 8mg/L at 20℃, and it can dissolve more than 50% in organic solvents such as benzene, xylene, acetone, methylene chloride, methanol, n-ethane, ethyl acetate and corn oil. Kow 20000(20~22℃PH7). Decomposes 0.5~2.0% in 30 days at 54℃. Degrades on glass plates in sunlight, DT50 is 3 hours.
Stable in neutral and weakly acidic media, unstable in strong acidic and alkaline media. Carbofuran is a highly efficient, broad-spectrum insecticide and a low-toxic derivative of carbofuran, which has systemic, contact and stomach poisoning effects. It can be widely used to control rice water weevils, thrips, borers, cotton aphids, onion flies, diamondback moths, etc. It can be used as a soil treatment agent to control underground pests and foliar pests. However, due to problems such as poor stability and short residual effect, this problem needs to be solved through sustained-release granules.
However, the current slow-release granule preparation technology has the disadvantage of low loading rate of bentonite pesticides, and it is difficult to achieve controlled release of propylcarbosulfan, making it consistent with the occurrence patterns of pests and diseases, and achieving safe, reasonable, economical and The purpose of using pesticides effectively.
Structure
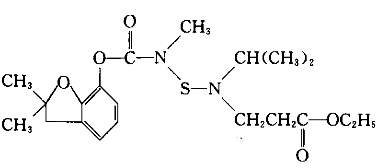
Apply[1]
Broad spectrum insecticide. Generally, 2 to 3 kilograms of 5% granules are used per acre, and 1,500 to 3,000 times of 20% emulsifiable concentrate is used for spraying to control fruit tree aphids. It is used in dry land. When applying pesticides, the soil or air humidity is high, which is conducive to the effectiveness of the medicine; low temperature and dryness affect the full effectiveness of the medicine. To control borer pests, pesticides must be applied at a certain time before the pests penetrate the crop.
(1) Soil treatment: Use 800-1,200 grams of 5% granules or 400-600 grams of 10% EC per acre to control corn pests, flea beetles, potato beetles, and potato beetles on sugar beets and vegetables. Wireworms, diamondback moths and aphids, etc.
(2) Seed treatment: Use 0.4 to 2 kg of 20% EC for every 100 kg of seeds.
Specifications[1]
3%, 5%, 10% granules, 10%, 20% emulsifiable concentrate.
How to use[3]
1. Rice pests: To control dead hearts caused by stem borer, stem borer and giant borer, apply 30-37.5kg of 5% granules per hectare before the peak hatching period. To prevent white ears and insect-damaged plants caused by the three-in-one borer and the giant borer, during the egg hatching period, use 30-45kg of 5% granules per hectare and apply by broadcast. To control brown rice lice, white-backed rice lice, etc., during the booting stage of rice, apply 30kg of 5% granules per hectare. When spreading the granules, keep the water layer in the field for 3 to 4 days, and the efficacy period can reach more than one month. To control rice weevil beetles and rice leaf rollers, use 2250-3750ml of 20% EC per hectare, mixed with water and spray.
2. Cotton pests: To control corn borer, apply 30-45kg of 5% granules per hectare during the end of the heart leaf stage and the pollination stage when corn borer eggs hatch. To control cotton aphids, apply it to cotton plant holes when transplanting cotton seedlings. Apply 1.2 to 2kg of 5% granules per acre. The control effect reaches 90% 30 days after application and about 70% after 40 days. Application method: Use an animal-powered sowing cog to install a granule application component, so that the granules and seeds can be applied into the soil simultaneously or sown in holes on demand.
3. Sugarcane pests: To prevent and control sugarcane borers, in the sugarcane seedling stage, when the first generation of sugarcane borers occurs, apply 45kg of 5% granules per hectare, spread it on the base of the sugarcane seedlings, and cover it with soil. It can also be treated simultaneously. Cane Seedling Black Cane Turtle.
4. Corn pests: To control corn borer, apply 30 to 45kg of 5% granules per hectare at the end of the heart leaf stage and the pollination stage when the second and third generation eggs of the corn borer are in full bloom. Apply once each to achieve a control effect of More than 90.
5. Sugar beet pests: To control beet wireworms, jumpers, root chews, etc., use 20-30kg of 5% granules per hectare. When sowing sugar beets, apply it at the same time as the seeds. Or apply the fertilizer in a ditch at the base of the sugar beet seedlings, then cover it with soil.
6. Vegetable pests: To control vegetable aphids, cabbage caterpillars, diamondback moths, twenty-eight-spotted ladybugs, onion thrips and potato beetles, use 2250-3750ml of 20% EC per hectare, mixed with water and spray.
7. Fruit tree pests: To control citrus aphids, peach aphids, peach heartworms, etc., use 20% EC 300-400 times liquid spray. To control various scales on fruit trees, spray 20% EC 300-400 times during the first and second instar nymph stages.
Pharmacological effects[3]
Carbofuran is a systemic, broad-spectrum insecticide that has a contact killing effect on pests and is mainly gastric poisoning. Carbofuran is a sulfinyl derivative of carbofuran. Its N-substituent β-aniline ethyl ester is linked to carbofuran through a sulfur atom. Its toxicity to some piercing and sucking mouthpart pests is similar to that of carbofuran. Budweur is similar, but its toxicity to some lepidopteran pests is higher than that of carbofuran, its duration of effect is similar to that of carbofuran, and its toxicity to mammals is greatly reduced. Carbosulfan has a rapid systemic conduction effect and can be absorbed by the roots of crops and transmitted to the stems and leaves above ground. When pests chew and suck the juice of poisonous plants or bite poisonous tissues, they are absorbed in the body. Cholinesterase is inhibited, killing the pest.
Toxicity[3]
Acute oral LD50: male rats 138mg/kg, male mice 175mg/kg, dogs 300mg/kg. The acute percutaneous LD50 in rats is greater than 2000mg/kg. The inhalation LC50 for rats is 0.24mg/L. Subcutaneous injection of mice LD50 is greater than 288mg/kg. No irritation to rabbit skin, slight irritation to eyes. The no-effect doses in the 2-year feeding trial of rats and dogs were 1.5 mg/kg·day and 2.5 mg/kg·day respectively. The acute oral LD50 of chicken is 92.2mg/kg. Low toxicity to birds. Fish poison LC50 (48 hours) 0.65mg/L. Daphnia LC50 (3 hours) is greater than 10mg/L, and bee toxicity is 0.28μg/head.
Notes[3]
1. Granules must go through a process of dissolution and absorption on crops. The appropriate application period should be about 3 days earlier than that of liquid agents. Especially for borer pests, pesticides should be applied before they penetrate the crops. When the soil is dry or wet, When it is low, drought-resistant irrigation is beneficial to the effectiveness of the medicine.
2. The application of carbofuran in rice fields cannot be mixed with propanil. The application of propanil should be carried out 3 to 4 days before the application of carbofuran in rice fields, or one month after the application.
3. Symptoms such as headache, sweating, weakness, chest depression, vision loss, stomach pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and body convulsions may occur when poisoning with Ankri. During use, if any medicine comes into contact with your body, you should immediately take off your clothes and wash the contaminated skin with soapy water; if any medicine splashes into your eyes, you should immediately rinse with plenty of water. If you are poisoned by accidental ingestion, you should drink 1 to 2 cups immediately. Clear water and detoxify with atropine.
Quality standards[3]
Ankli 5% granules are composed of the active ingredient Ankli, carrier, solvent, and dye. The appearance is blue fine particles. Usually 1978mg/kg, acute transdermal LD50>2000mg/kg. The toxicity of the preparation to fish is very low, with the TLm of carp being 117 mg/L.
Analysis method [3]
Product analysis uses HPLC or GC. Residues and metabolites, carbofuran analogues were determined by GC, and soil residues were determined by HPLC.
degradation metabolism[3]
Carbosulfan is metabolized very quickly in the body of animals and is excreted in the urine after metabolism. It is easily converted into carbofuran and 3-hydroxycarbofuran in soil and plants, followed by hydrolysis, oxidation, and ring cleavage of carbofuran. The half-life in soil is 2 to 30 days. The half-life on plants is about 10 days.
Allowable residue [3]
According to foreign introduction, the allowable daily intake (ADI) is 0.01mg/kg, the maximum residue level (MRL) in brown rice is 0.2mg/kg, and the maximum residue level (MRL) in cottonseed is 0.1mg/kg. The 5% granules are 0.5 mg/kg in rice, 0.2 mg/kg in rice, 1 mg/kg in vegetables, and 0.5 mg/kg in fruits.
Preparation[3]
N-Isopropyl-β-alanine ethyl ester reacts with sulfur dichloride, and the product reacts with carbofuran to prepare propylthiocarbofuran. The reaction formula is as follows:
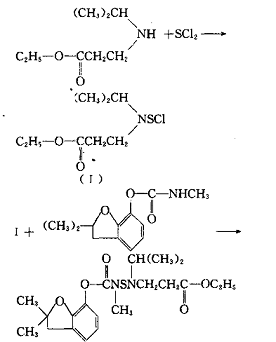
Main reference materials
[1] Pesticide Operation and Use Knowledge Manual
[2] Li Tao; Li Min; Gao Hengxu; Chen Jiuxing; Ou Xiaoming; Du Shenghua. Carbosulfan sustained-release granules and preparation method. CN201310712284.2, application date 2013-12-20
[3] Pesticide product list



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
