Background and overview[1]
P-Nitrotoluene, also known as 1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene, is a light yellow crystal with a melting point of 54.5°C and a boiling point of 238.3°C. Easily soluble in benzene, ether, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, soluble in ethanol, insoluble in water, and can evaporate with water vapor. Toxic! Mainly used in the manufacture of p-toluidine, toluidine, p-nitroformic acid, p-nitrotoluene-2-sulfonic acid, 3-chloro-4-nitrotoluene, etc. It is used as an intermediate for dyes, medicines, pesticides, synthetic materials, auxiliaries, etc. This product is obtained by nitration of toluene with mixed acid and separation. At the same time, o-nitrotoluene is co-produced.
Apply [2-4]
1. Synthesis of p-bromobenzaldehyde using p-nitrotoluene
P-Bromobenzaldehyde is an important pharmaceutical and dye intermediate. The existing methods for synthesizing p-bromobenzaldehyde mainly use p-bromotoluene as raw material. One method is to generate benzyl dibromide through photobromination reaction, which is then hydrolyzed. This method has been industrialized; the other method is to use trifluoride. Cerium methyl sulfate is obtained by oxidation with oxidant. Their common shortcomings are the high cost of raw materials, and the former uses highly volatile and hazardous liquid bromine, while the latter uses an oxidation method that is difficult to control industrially.
CN97106992.1 proposes a method for synthesizing p-bromobenzaldehyde using p-nitrotoluene as raw material. The invention uses p-nitrotoluene as raw material, and under the catalysis of a phase transfer catalyst, a disproportionation reaction occurs with sodium polysulfide solution to generate p-aminobenzaldehyde, and then the p-aminobenzaldehyde is acidified and diazotized in bromide Under the catalysis of copper or copper, p-bromobenzaldehyde is generated. Sodium polysulfide solution is generated by the reaction between sodium sulfide (Na2S.9H2O) and elemental sulfur. The molar ratio of sodium sulfide to sulfur is 1:2-1:4. Sodium polysulfide and p-nitrotoluene in a 95%-65% ethanol solution generate p-aminobenzaldehyde under the action of a phase transfer catalyst, and a small amount of p-toluidine is produced. The molar ratio of sodium polysulfide to p-nitrotoluene is 1:3-1:5. The amount of phase transfer catalyst added is 1%-5% of the amount of p-nitrotoluene participating in the reaction. It takes 1 mol of p-nitrotoluene to participate in the reaction. 95% ethanol 400-600ml, reaction temperature is 80-90°C. Under the above conditions, the yield of p-aminobenzaldehyde is >90%.
The phase transfer catalyst used is one or two of tetrabutylammonium bromide, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, tetrabutylammonium iodide, N-dimethylformamide, and Tween. Mixtures, using mixed phase transfer catalysts are more effective. The prepared p-aminobenzaldehyde is steam distilled, cooled and crystallized to obtain a dehumidified product, which can be directly used in the next step of the reaction without drying. For the acidification of p-aminobenzaldehyde, sulfuric acid is used as the acidifying agent and sodium nitrite is used as the diazotizing reagent. After the diazotization is completed, drop the diazonium salt solution into the newly prepared copper bromide hydrobromic acid solution or the newly prepared reduced copper hydrobromic acid suspension. After the dripping is completed, slowly heat the solution to 60°C and keep it warm for a period of time. hours, carry out steam distillation, filter and wash the distillate to obtain colorless or light yellow p-bromobenzaldehyde. Purity >98%. To participate in the reaction, 1 mol of p-aminobenzaldehyde requires 0.5-1 mol of cuprous bromide or 0.05-0.1 mol of reduced copper, and 2-3 mol of hydrobromic acid is required. The preparation of cuprous bromide adopts the usual method. The yield of p-bromobenzaldehyde relative to p-nitrotoluene is 55-65%. The invention provides a method for synthesizing p-bromobenzaldehyde using p-nitrotoluene as raw material. Using this method to synthesize p-bromobenzaldehyde has low raw material cost, easy industrialization, and product purity reaching 99%.
2. Used to synthesize DSD acid
4,4′-Diaminostilbene-2,2’disulfonic acid (DSD acid for short) is an amphoteric compound that contains not only the acidic group sulfonic acid group, but also the basic amino group. It can directly undergo a condensation reaction with cyanuric chloride, or can undergo a coupling reaction with most aromatic compounds after diazotization. Therefore, using DSD as raw material, a series of direct dyes, acid dyes and reactive dyes can be synthesized.
At present, the process route used by most domestic manufacturers to synthesize DSD acid is to sulfonate p-nitrotoluene to generate p-nitrotoluene orthosulfonic acid (NTS acid for short), and then oxidize it in an alkaline medium to generate 4,4′ -Dinitrostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid (dinitro acid or DNS acid for short) is finally reduced to obtain DSD acid. CN201510732494.7 provides a DSD acid synthesis process that combines electrodialysis with bipolar membrane electrodialysis to replace the salting out step in the traditional process. The process flow is simple, the operation is simple, the conditions are mild, and the discharge of process wastewater is reduced. The amount of raw material salt used reduces the salt content in subsequent reactions, and at the same time makes full use of the inorganic resources produced in the process, improves the quality and yield of the product, and reduces the process cost.
A DSD acid synthesis process, which is characterized by including the following steps: (1) p-nitrotoluene orthosulfonic acid is generated through a sulfonation reaction; (2) p-nitrotoluene orthosulfonic acid is generated in alkaline The oxidative condensation reaction liquid is obtained through oxidative condensation reaction in the medium; the oxidative condensation reaction liquid is subjected to electrodialysis treatment to obtain the intermediate product 4,4′-dinitrostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid (DNS acid). Organic liquid and salt water; (3) The organic liquid in step (2) is subjected to reduction reaction and acid precipitation to prepare the finished product of DSD acid; the salt water is processed by a bipolar membrane electrodialysis system to prepare a sulfuric acid aqueous solution and a sodium hydroxide aqueous solution. and dilute brine; sulfuric acid aqueous solution and sodium hydroxide aqueous solution can be reused in the DSD acid synthesis process respectively.
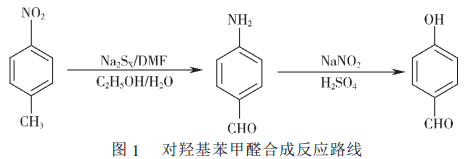
3. Synthesis of p-hydroxybenzaldehyde from p-nitrotoluene
As the uses of p-hydroxybenzaldehyde become more and more widespread, the market demand at home and abroad is also increasing.As a result, domestic and foreign manufacturers and research departments have been conducting long-term and in-depth research on its production technology, and there have been a large number of research reports. There are currently 6 main production processes reported at home and abroad, of which two production processes deserve the most attention: one is a two-step classic synthesis process using p-nitrotoluene as raw material, first carrying out oxidation and reduction, and then carrying out diazotization reaction. , the synthesis reaction route is shown in Figure 1; the other is a new synthesis process that uses p-cresol as raw material and synthesizes the target product through pure oxygen oxidation under the action of a mixed catalyst of cobalt and copper compounds.
Main reference materials
[1] Concise Dictionary of Fine Chemicals
[2] CN97106992.1 A method for synthesizing p-bromobenzaldehyde
[3] CN201510732494.7 A DSD acid synthesis process
[4]Zhou Hui, Dong Shichang, Li Liwei. Process improvement for synthesizing p-hydroxybenzaldehyde from p-nitrotoluene[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Industry, 2010, 19(06):16-17.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
