Background[1][2]
Diphenylphosphine chloride (CDPP) is one of the important raw materials for the production of photoinitiator TPO. Its synthesis is obtained through the Friedel-Crafts reaction of benzene and phosphorus trichloride under the catalysis of aluminum trichloride. After the reaction, aluminum trichloride will form a complex with the product, so it is necessary to add the decomplexing agent sodium chloride to free the product CDPP. This will produce a large amount of sodium tetrachloroaluminate solid waste, and this part of the solid residue will be due to Containing a very small amount of CDPP causes a strong odor, and every 1 ton of CDPP produced produces approximately 3 tons of solid waste. Therefore, how to reasonably handle this solid waste is an urgent problem for CDPP production companies to solve.
Some studies have comprehensively treated the solid residue generated during the production of diphenylphosphine chloride, and characterized and experimentally verified the recovered sodium chloride. Experiments have proven that the recovered sodium chloride can be directly It was reapplied to the decomplexation reaction of diphenylphosphine chloride, and the yield of sodium chloride was 92.8%. The aluminum chloride obtained after dissociation is processed to prepare a water treatment agent PAC. There is no significant difference between the water treatment effect of homemade PAC and the treatment effect of purchased PAC. Through treatment, the problem of solid slag can be solved, the purpose of waste reuse can be achieved, and the pollution to the environment can be reduced. The treatment operation process is simple and has certain industrial application prospects.
Diphenylphosphine chloride is an important organophosphorus chemical product and can be used industrially to produce photoinitiator TPO, diphenylphosphine oxide, catalysts, etc. The current industrial synthesis method uses benzene and phosphorus trichloride as raw materials, reacts under the catalysis of anhydrous aluminum trichloride, and the generated diphenylphosphorus chloride is complexed with aluminum trichloride. Oxygen hexacyclic ring, crushed sodium chloride or potassium chloride react with aluminum trichloride to dissociate diphenyl chloride.
The disadvantage of this method is that the decomplexation process is troublesome and a large amount of water-sensitive solid waste is generated. Since the product is solid-liquid separation, it cannot be completely separated. Therefore, the yield of the product is low, the cost is high, and the environmental protection problems are serious. As a result, the product cannot be mass-produced. It has also been reported that diphenylphosphine chloride can be generated through high-temperature disproportionation of phenylphosphine dichloride under the catalysis of aluminum trichloride. This method requires high-temperature hydrochloric acid-resistant equipment. In addition, since phenylphosphine dichloride is used as the raw material, the raw material High costs lead to high product costs.
Apply[3][4]
Diphenylphosphine chloride (CDPP) is an important intermediate that is widely used in the preparation of anti-UV agents, organophosphorus flame retardants, antioxidants, plasticizers and asymmetric synthesis catalysts.
1. Prepare a diphenylphosphine cumyl ester.
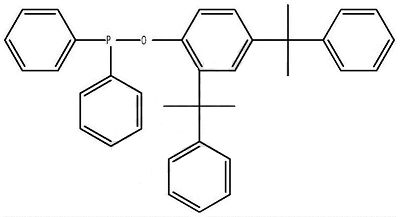
The synthesis method is to pass protective gas into the mixture of 2,4-dicumylphenol and the solvent, and dropwise add the mixture of diphenylphosphine chloride and the solvent. After the addition is completed, the reaction is kept warm; after the reaction is completed, stop Pass protective gas, cool down, and evaporate the solvent under normal pressure or reduced pressure to obtain a light yellow viscous liquid; then add a crystallizer to the viscous liquid, and then add an appropriate amount of activated carbon, keep it warm for 30 minutes under reflux, filter while it is hot, and cool the filtrate Finally, a white solid precipitates, which is filtered and dried to obtain the product.
The synthesis process of the present invention avoids the shortcomings of using an acid binding agent in the conventional reaction of synthesizing phosphite compounds. The by-products generated by the reaction are actively squeezed out by the introduced protective gas, eliminating the need for suction filtration, washing, and filtration to remove the generated products. The amine salt and other procedures are used. In addition, the crystallizing agent is used to directly crystallize the product, which avoids the environmental pollution problems caused by the existing use of organic solvents to wash the product multiple times.
2. Prepare a photoinitiator TPO.
The formula is as follows: 22.5% diethylaniline, 7.5% anhydrous methanol, 34% diphenylphosphine chloride, 36% 2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl chloride. The method is as follows: 1. Combine the two Stir and mix ethylaniline and anhydrous methanol evenly; 2. Heat the material to 20°C, slowly add diphenylphosphine chloride dropwise and keep it warm for 2 hours; 3. Take out the material and filter it for later use; 4. Add 2, 4, 6 – Stir trimethylbenzoyl chloride evenly; 5. Heat the material to 80°C, slowly add the materials to be used in step 3 dropwise, and then keep the temperature for 1 hour; 6. Use a suction filtration tank to filter to obtain the photoinitiator TPO. The process is simple and does not require the use of flammable and explosive solvents such as toluene during the reaction. It is safe, reliable and beneficial to energy conservation and environmental protection.
Preparation[1][5]
Method 1: OneThe environmentally friendly synthesis method of diphenylphosphine chloride is as follows:
A. Reaction operation: Add phosphorus trichloride, benzene and aluminum trichloride into three-necked bottles respectively, pass in nitrogen for protection, stir vigorously, raise the temperature to 140-150°C, maintain reflux, and release a large amount of White smoke, until the white smoke disappears, the temperature begins to cool down to room temperature;
B. Post-processing operation: : Add organic solvent to the reaction solution in step A and stir for 0.5h, then add the decomplexing agent β-triethyl chlorophosphate dropwise, complete the dropwise addition for 0.5h, stir for 1.0h, and let stand for 1.0 h, separate the lower decomplexing agent layer, and distill the organic solvent layer under reduced pressure to obtain crude diphenylphosphine chloride. Distill the crude diphenylphosphine chloride under high vacuum to obtain pure diphenylphosphine chloride. , the organic solvent is one of heptane, phosphorus trichloride or phosphorus oxychloride;
C. Recovery operation: Drop the separated decomplexing agent layer into the three-necked bottle containing water, and stir vigorously. After the dropwise addition, stir for 1.0h, let stand for 0.5h, separate, and move to the lower decomplexing agent layer. Add anhydrous calcium oxide, let it stand for 3.0 hours, and filter; continue to add anhydrous sodium sulfate to the decomplexing agent layer, let it stand for 4.0 hours, filter, and heat and evaporate the separated water layer to dryness to obtain alumina. In order to achieve better results, the molar ratio of phosphorus trichloride, benzene and aluminum trichloride in step A is 1:1:1.0~1.3.
Method 2: Use Lewis acid room temperature ionic liquid to catalyze the reaction of benzene and phosphorus trichloride to synthesize diphenylphosphine chloride. The specific process steps are as follows:
Step 1: Synthesis of Lewis Acid Room Temperature Ionic Liquid: The synthesis steps are: Mix quaternary ammonium salt and anhydrous aluminum trichloride in batches at a molar ratio of 1:1 to 1:4 under the protection of dry nitrogen. , the mixing process controls the temperature between 40 and 160°C, and maintains it at 40 to 160°C for 3 hours to obtain a Lewis acid room temperature ionic liquid. The quaternary ammonium salt can be triethylamine hydrochloride, N-alkylpyridine chloride or 1-methyl-3-alkyl imidazole, etc.
Step 2: Synthesis of diphenylphosphine chloride:
(1) According to the molar ratio of phosphorus trichloride: benzene: aluminum trichloride in ionic liquid = 0.8 1.5: 1.5~2.5: 0.01~1, combine phosphorus trichloride, benzene and the amount obtained by the first step method. The prepared ionic liquids are mixed, heated to reflux, and maintained for 6 to 24 hours.
(2). After cooling down the reaction mixture, let it stand for 30 to 12 minutes to allow the reactants to separate into layers.
(3) The above reactants are separated into two layers, in which the ionic liquid layer is poured into the extraction kettle, and the phosphorus trichloride layer is poured into the product crude distillation kettle.
(4) According to the volume ratio of ionic liquid layer: extraction agent = 1 to 3:1, add the extraction agent to the extraction kettle, extract three times, and finally pour the ionic liquid layer into the ionic liquid storage tank, and add each extraction liquid Pour the product into the crude steamer. The extraction agent can be petroleum ether, phosphorus trichloride or a mixture of phosphorus trichloride and petroleum ether in any proportion.
(5) Distill the liquid in the crude distillation kettle under normal pressure to evaporate phosphorus trichloride, extraction agent and benzene. When the temperature rises to 90°C, no phosphorus trichloride, benzene and extraction agent are evaporated. Obtain the crude diphenylphosphine chloride after atmospheric distillation.
(6) Distill the above-mentioned crude diphenylphosphine chloride under reduced pressure, and distill out the remaining steamed phosphorus trichloride, extractant and benzene. Under a vacuum of 450mmHg, the liquid phase temperature rises to 90-120°C. When no low boiling point component is distilled, increase the vacuum to 600~720mmHg, collect the fractions at a liquid phase temperature of 90-120°C to obtain phenylphosphine dichloride, and collect the fractions at a liquid phase temperature of 140-100°C to obtain refined dichloride. Phenylphosphine chloride.
The third step: recovery of ionic liquid, the steps are: heat up the ionic liquid in the ionic liquid storage tank and distill it under normal pressure, collect and recover phosphorus trichloride, benzene and extraction agent, and wait until the temperature rises to 90°C. When phosphorus trichloride, benzene and petroleum ether are evaporated, perform vacuum distillation. When the vacuum is 450~600mmHg and the liquid phase temperature rises to 100~130°C and no low boiling point components are distilled out, cool down to obtain the ionic liquid. The recovered ionic liquid replaces the ionic liquid prepared in the first step, and the second step and the second polymerization step are repeated to prepare diphenylphosphine chloride; the number of times the ionic liquid is reused is 1 to 8 times.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201210473945.6 A synthesis method of diphenylphosphine chloride
[2] Comprehensive recovery and utilization of sodium tetrachloroaluminate in diphenylphosphine chloride wastewater
[3] CN201410269635.1 A kind of diphenylphosphine cumyl ester and its synthesis method
[4] CN201410096817.3 Preparation method of photoinitiator TPO
[5] CN201110426418.5 Environmentally friendly synthesis method of diphenylphosphine chloride



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
