2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid, also known as 5-hydroxysalicylic acid, commonly known as DBH, also known as gentisic acid, is a polyhydroxycarboxylic acid, which is the secondary metabolite of salicylic acid after renal metabolism. product. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is white needle-like crystal, soluble in hot water, ethanol and ether, but insoluble in chloroform, benzene and carbon disulfide. When heated for a long time above 150℃, it decomposes into carbon dioxide and hydroquinone, which is unstable in the air and turns blue when exposed to ferric chloride.

2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is a hydroquinone compound that is prone to oxidation reactions and is often used as an antioxidant excipient in the pharmaceutical industry. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is also an antipyretic and analgesic and an important pharmaceutical intermediate.
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid is also a commonly used matrix in matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry, and it is widely used. At present, there are few reports on the synthesis of 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid. There have been reports in the literature that the product was synthesized using benzoic acid as raw material through chlorination, hydrolysis and other steps. However, there are five kinds of products synthesized by this method, and the products are difficult to separate. , resulting in a final yield of only 5%, making it difficult to achieve industrial production.
The Kolbe-Schmidt reaction of hydroquinone is commonly used in industry to prepare 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid. However, the synthesis yield of this method is low, the purity is not high, and it is difficult to meet the requirements of industrial production. Therefore, a new method is sought. The synthesis method is extremely important.
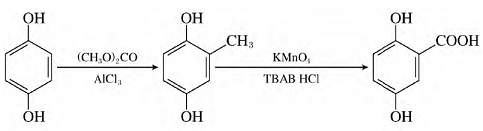
According to research, hydroquinone is used as raw material and 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid is synthesized through a two-step reaction of methylation and oxidation. The synthesis reaction steps are simple, the yield is as high as 90.3%, and the purity is as high as 99.6%. It can meet market demand and is suitable for large-scale industrial production. The synthetic route of the target product is as follows:
Using hydroquinone as raw material, the target product 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid was synthesized through two-step reactions of methylation and oxidation. The optimal conditions for the methylation reaction are: the amount of catalyst ALCL3 is 130% of the amount of substrate, the reaction temperature is 130°C, and the reaction time is 4 hours. The optimal conditions for the oxidation reaction are: the dosage of catalyst TBAT is 5% of the substrate dosage, the reaction temperature is 100°C, and the reaction time is 4 hours. Under optimal conditions, the yield of 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid can reach 90.3%.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
