1. Polyisocyanate
Polyurethane foamThe most commonly used polyisocyanate in industrial production is toluene diisocyanate (TDI), polymethylene polyphenyl isocyanate (PAPI), diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI) and liquefied MDI (L-MDI), etc.
TDI is mainly used in the foam plastic industry to produce polyurethane soft foam. MDI has greater reactivity than TDI and less volatile toxicity. Some liquefied modified MDI is used as a substitute for TDI in the production of polyurethane soft foams, such as the manufacture of high-density polyurethane soft foams and semi-rigid foams or microporous polyurethane elastic materials. .
PAPI is also called crude MDI and polymerized MDI. The average molecular weight of typical PAPI products is in the range of 300 to 400, and its NCO mass fraction is 31% to 32%. The average functionality of low-viscosity PAPI is generally between 2.5 and 2.9. In the field of foam plastics, PAPI and modified PAPI are mainly used to produce various polyurethane hard foams, and a small amount is used to produce high-resilience soft foams, whole-skin foams, and semi-rigid foams. It can be mixed with TDI to produce cold-cured, high-resilience foam plastics.
2. Polyether and polyester polyols
(1)Polyether polyol
Polyether polyols used in soft foam are generally long-chain, low-functionality polyethers. The functionality of polyether polyols in soft foam formulations is generally 2 to 3, and the average molecular weight is between 2000 and 6500. The most commonly used polyethertriol in soft foam is polyethertriol, which generally uses glycerin (glycerol) as the starting agent and is obtained by ring-opening polymerization of 1,2-propylene oxide or copolymerization with a small amount of ethylene oxide. The molecular weight Generally between 3,000 and 7,000. Among them, high-activity polyether is mainly used for high-resilience soft foam, and can also be used for foam products such as semi-rigid foam. A small amount of polyether diol can be used as an auxiliary raw material and mixed with polyether triol in soft foam formulations. Low unsaturation and high molecular weight polyether polyols can be used in the production of soft foam to reduce the amount of TDI.
For rigid foam formulations, polyether polyols with high functionality and high hydroxyl value are generally used to produce sufficient cross-linking and rigidity. The hydroxyl value of rigid foam polyether polyol is generally 350~650 mgKOH/g, and the average functionality is above 3. The general hard foam formula is mostly a mixture of two polyethers, with an average hydroxyl value of around 400mgKOH/g.
Semi-rigid foam formulas generally use some high molecular weight soft foam polyethers, especially highly active polyether polyols, and some high functionality low molecular weight rigid foam polyethers.
( 2) polyester Polyol
Ordinary low-viscosity aliphatic polyester polyols such as polyglyceryl adipate with a hydroxyl value of about 56mgKOH/g Alcohol ester diols, or slightly branched polyester polyols, can be used to make polyester-based polyurethane flexible foams. Polyester polyols are highly reactive. At present, polyester PU block foam is only used in a few areas such as clothing auxiliary materials.
Aromatic polyols synthesized from dibasic acids such as phthalic anhydride (or / and terephthalic acid, etc.) and small molecular diols or polyols such as diethylene glycol, Those with high hydroxyl value can be used to produce polyurethane and polyisocyanurate rigid foams. Phthalic anhydride polyester diols with lower hydroxyl values can also be used for high resilience applications.t>A very ideal foaming agent in production. From the1960s to the early 1990s, CFC-11 was widely usedPolyurethane foam foaming agent. But in the 1970s, scientists discovered that CFC-11 emitted in the atmosphere could slowly destroy the ozone layer, which attracted the attention of environmentalists around the world. The main types of blowing agents currently used as alternatives to CFC-11 include HCFC (hydrochlorofluorocarbon), HFC (hydrofluorocarbon), HC (alkane), liquid CO2 and water.
The following tableis some commonTypical physical properties and comparison of HCFC blowing agent and CFC-11.
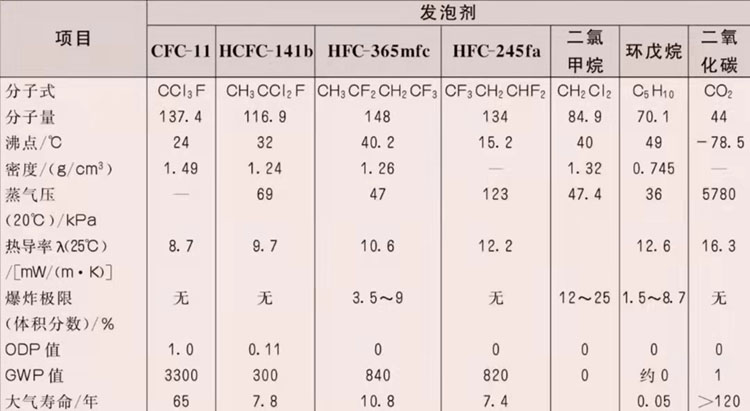
Note: Greenhouse effect potential (GWP) is expressed in terms of CO2 GWP=1 meter. The density is measured at 20°C, and the density of low-boiling point HCFC is measured after liquefaction under pressure.
( 2) Foam stable Agent
Productionpolyurethane When foaming, the foam stabilizer (or foam stabilizer) is a An indispensable component. It increases the mutual solubility of each component and plays the role of emulsifying foam materials, stabilizing foam and regulating cells.
Foam stabilizers are surfactants and include non-silicon compounds and organic silicon compounds. Most of the currently used foam stabilizers are polysiloxane-oxyalkylene block copolymers, which are polyether-modified silicone surfactants and are sometimes commonly known as “silicone oil” in the industry. Due to the wide range of changes in the structural composition of this type of surfactant and its good use effect, currently<font face=" Polyurethane foamPolyether-modified silicone has been widely used in the industry Surfactants act as foam stabilizers.
( 3) Opening Agent
Get openingsPolyurethane foammethod: the first is to use a suitable catalyst, Make the gel reaction and foaming reaction reach the required balance. When the foam material rises to the highest point, the wall membrane of the cells is not strong enough to seal the bubbles inside, and the gas breaks out of the wall to form an open-cell foam structure; The second is to use suitable polyether polyol raw materials to form open-cell foam; the third is to use a small amount of pore-opening agent when the catalyst and main raw materials are not enough to solve the problem, so that the urea formed by water foaming is dispersed to obtain Foam plastic with a certain open cell ratio.
Cell-opening agent is a special type of surfactant, which generally contains hydrophobic and hydrophilic segments or groups. Its function is to reduce the surface tension of foam, promote cell rupture, and improve Polyurethane foam‘s open cell ratio can improve the shrinkage problems of soft, semi-rigid and rigid foam plastic products caused by closed cells. Due to the high cross-linking density and the strong strength of the cell wall membrane in the foaming process, ordinary polyurethane rigid foam generally has a closed cell structure, but by adding a cell opening agent, open-cell rigid foam can be produced Polyurethane foam, used for silencing, filtering and other purposes.
Early hydrophobic liquid paraffin, polybutadiene, dimethyl polysiloxane, etc. can be used as foam stabilizers and pore opening agents. Paraffin dispersions and polyethylene oxide can also be used as pore opening agents. Currently, they are mostly used Polyoxypropylene-oxyethylene copolyether, polyoxyalkylene-polysiloxane copolymer, etc. with special chemical composition are used as pore opening agents.
( 4) Softener
Using softeners in the production of polyurethane soft foam with high water content formula can suppress the stiffness of the foam caused by excessive urea groups. Foam softening modifier has a softening effect. The use of softening agents can reduce the amount of isocyanate and thus reduce the foam hardness. It is used for soft materialsPolyurethane foamProduction. Commercial softeners generally contain ingredients such as special polyethers, special polyols and water.
span>Polyurethane foam, used for silencing, filtering and other purposes.
Early hydrophobic liquid paraffin, polybutadiene, dimethyl polysiloxane, etc. can be used as foam stabilizers and pore opening agents. Paraffin dispersions and polyethylene oxide can also be used as pore opening agents. Currently, they are mostly used Polyoxypropylene-oxyethylene copolyether, polyoxyalkylene-polysiloxane copolymer, etc. with special chemical composition are used as pore opening agents.
( 4) Softener
Using softeners in the production of polyurethane soft foam with high water content formula can suppress the stiffness of the foam caused by excessive urea groups. Foam softening modifier has a softening effect. The use of softening agents can reduce the amount of isocyanate and thus reduce the foam hardness. It is used for soft materialsPolyurethane foamProduction. Commercial softeners generally contain ingredients such as special polyethers, special polyols and water.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
