Recently, Mitsubishi Chemical Group (MCG Group) announced that the company has acquired CPC SRL, a well-known Italian carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) automotive parts supplier.
(CPC), the transaction is subject to regulatory approval and is expected to close by the end of 2023.
As early as 2017, Mitsubishi Chemical issued a statement stating that its German subsidiary Mitsubishi Chemical Carbon Fiber and Composites
GmbH acquires 44% of CPC SRL’s shares.
CPC SRL has a range of expertise including component design and simulation, carbon fiber composite molding, tooling and mold design and manufacturing, coating composites and sub-component assembly.
Through the acquisition, Mitsubishi Chemical can leverage CPC’s distribution network and proprietary technology in the U.S. and European automotive markets to accelerate the application of the company’s carbon fiber composite materials in automotive parts, such as sheet forming compound (CF-SMC) and prepreg compression molding. (PCM). At the same time, both parties will commit to further cooperate to develop sustainable solutions, including bio-based and recycled carbon fiber intermediate materials.
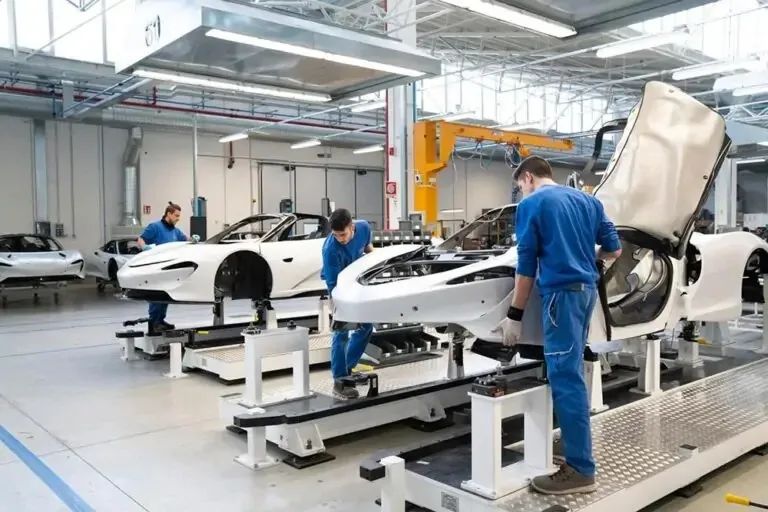

Image source: Mitsubishi Chemical official website
Japan’s Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings Group is currently one of the few manufacturers in the world that owns both PAN-based carbon fiber and pitch-based carbon fiber. By effectively utilizing PAN-based and Pitch-based raw materials, it can provide diversified carbon fibers, and its products cover continuous carbon fiber. Raw materials such as chopped carbon fiber and carbon fiber powder as well as end products.
In addition, Mitsubishi Chemical is good at SMC (CF-SMC), which is made by cutting carbon fiber into several centimeters long and then immersing it in resin. After rapid processing (usually within 2-5 minutes), it is molded through a molding process. Obtaining the parts required for production not only has the advantages of molding complex parts, but also takes into account the improvement of lightweight and productivity efficiency (reducing costs), greatly lowering the application threshold.
Picture source: Internet
At present, the carbon fiber reinforced composite material (CFRP) market is mainly used in aircraft and wind power blades, especially aircraft applications where the unit price of materials is high, accounting for more than half of the market. In recent years, CFRP has attracted more and more interest in the global automotive market due to its lightweight and carbon reduction effects. However, cost factors have prevented it from entering the mainstream automotive market.
Once prices and costs drop significantly, the future development potential is almost immeasurable. According to third-party forecasts, the market valuation of CFRP is expected to reach US$8 billion in 2023, and is expected to become a mainstream configuration in the global automotive market by 2025 (somewhat optimistic). At the same time, the demand for pressure vessels will also increase significantly.
It is also true that many carbon fiber companies around the world are making frequent moves. For example, the leading company Toray has announced production expansions many times this year and stated that it will increase the production capacity of its carbon fiber composite material (CFRP) production bases in the United States, South Korea and France by 2025, with an estimated investment of 100 billion yen.
Domestically, companies have also launched a wave of production expansion. As of the end of September 2023, the total domestic production capacity has increased to 117,200 tons, which is four times the production capacity in 2019, and will also grow rapidly. The products mainly involved in the new production line are T300 level 12K, 24K and 48K, and T700 level 12K.
Among them, large tows have become the main direction for domestic enterprises to expand production in the civil sector due to their characteristics of high strength, high modulus, low density and low cost. In addition, carbon thermal fields and pressure vessels are also key areas of investment.
With the steady growth of domestic production, Baichuan Yingfu statistics show that the average domestic carbon fiber import dependence dropped to 25.75% from January to August 2023. However, traditional entities have reduced downstream demand, pursued low prices, and export orders have significantly decreased. The market has fallen short of expectations, with apparent consumption falling by 0.36% year-on-year, and prices showing a unilateral decline.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
