Lim, Senior Researcher, Energy Aggregation Research Department, DGIST
The research team led by Sang-gyu has developed an environmentally friendly thermoplastic polyurethane with a bio-carbon content of up to 97%, which is a remarkable milestone.
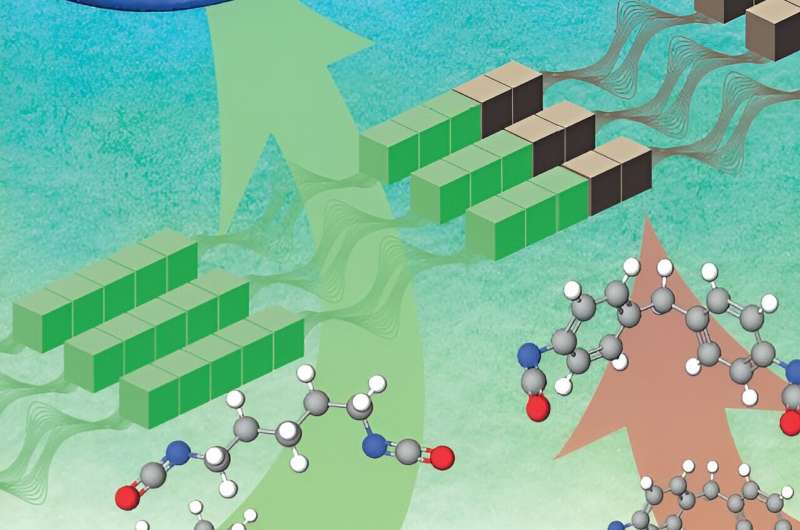
This breakthrough technology was developed in collaboration with Jung Jae-hoon of the new product development team and Jeon of the new business planning team at the Korea Textile Development Institute (KTDI)
Developed in collaboration with Cho-hyun, it is significant as it is a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based thermoplastic polyurethane.
Thermoplastic polyurethane is a remarkable material known for its outstanding mechanical properties including abrasion resistance, resilience, tensile strength and tear strength. Its versatility makes it widely used in various life and industrial fields, such as industrial sheets, screen protectors, bags, footwear, artificial leather and clothing materials, etc.
Currently, most TPUs are synthesized using petroleum-based polyols, isocyanates, and diols. Despite the excellent properties of petroleum-based raw materials, their extraction, manufacturing, use, and disposal processes cause environmental pollution. Therefore, worldwide efforts are being made to explore environmentally friendly alternatives based on biomass materials. However, developing bio-based products that match the properties of conventional TPUs faces enormous challenges.
In an excellent collaboration with KTDI, Lim
Sang-gyu’s research team has made a major breakthrough and developed an environmentally friendly thermoplastic polyurethane. To synthesize this environmentally friendly material, they utilized bio-based polyester polyol and butanediol, moving away from traditional petroleum-based materials.
This biomass-based thermoplastic polyurethane offers exceptional properties, including a biochar content of up to 97%, approximately 120,000
g/mol weight average molecular weight, 20MPa tensile strength and 587.2% tensile elongation.
Remarkably, these properties are comparable to existing petroleum-based thermoplastic polyurethanes, making the developed material a multifunctional candidate for a wide range of applications in daily life and in various industries. This environmentally friendly thermoplastic polyurethane is expected to be used in various fields such as industrial sheets, screen protectors, mobile phone cases, footwear, artificial leather and clothing materials.
Researcher Lim
Sang-gyu emphasized, “In order to distinguish their research from existing research on environmentally friendly thermoplastic polyurethanes, they carefully evaluated the chemical, thermal and mechanical properties of bio-based aliphatic isocyanates and changed their content ratios. Then These properties were compared to those of petroleum-based thermoplastic polyurethanes.”
He expressed optimism that the bio-based thermoplastic polyurethane developed through their research will be commercialized and widely used, especially in various fields using highly functional fiber materials.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
