Canadian startup Fortis3D is launching two new 3D printing materials for a range of industrial applications. Along with the launch of PA-GF20 and PK-GF20, Fortis3D has carried out a detailed analysis of the material properties of these two filaments, allowing engineers to understand their advantages and suitable application scenarios.
Using a background in polymer engineering, Fortis3D’s team of scientists and engineers created reinforced polyamide (PA), and polyketone (PK) 3D printing filaments that are stronger than other materials and have a lower glass fiber content.
Wayne, Business Manager at Fortis3D
“We found that most fiber-reinforced filaments on the market can produce relatively strong parts, but they are nowhere near as strong as traditional injection-molded fiber-reinforced resins,” Lam said. We want to make high-strength filaments available to more users. materials, not just those users with expensive industrial machines. With these two goals in mind, we developed these two materials to be the strongest on the market, allowing even users with mid-range printers to create High-strength parts.”,
PA-GF20Characteristics of PK-GF20
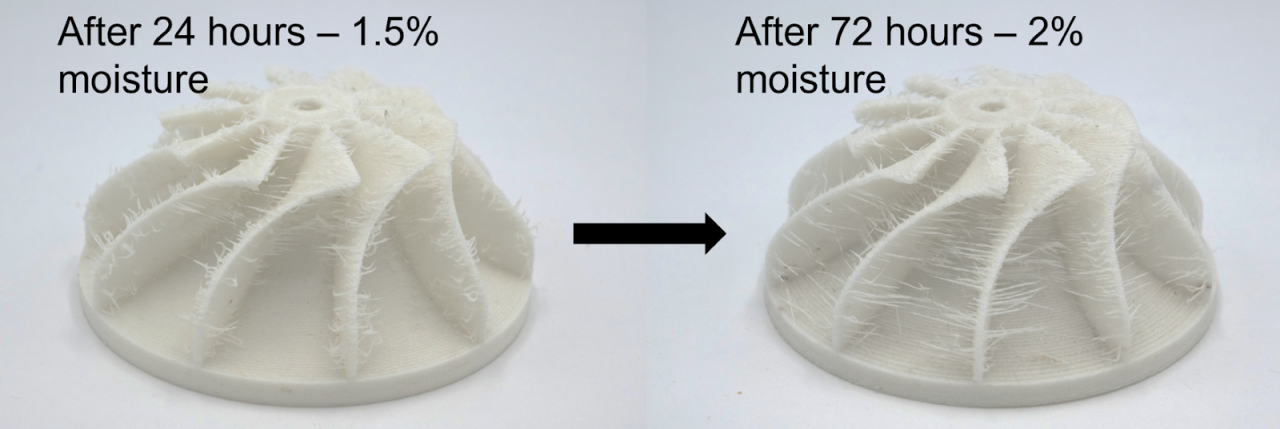

Fortis3D’s PA-GF20 and PK-GF20 chopped glass fiber reinforcements can be used to 3D print high-performance functional parts. In addition to their exceptional mechanical strength, the two materials are resistant to chemicals, high temperatures, impact and abrasion, making them durable in harsh environments. Applications for these materials range from industrial end parts to jigs.
Most other glass fiber reinforced filaments in the industry use very short (100-300µm) ground glass fibers that are mixed into various resins. Although they have good strength and printability, they can be very brittle. Longer lengths of chopped glass fibers (3mm) provide very high strength while retaining more of the toughness of the base plastic material, but are more challenging to mix. Both types of fibers typically break more during compounding, resulting in shorter fibers in the final product; therefore precautions must be taken during processing to minimize fiber breakage.
3DTechnical data of printing materials PA-GF20 and PK-GF20
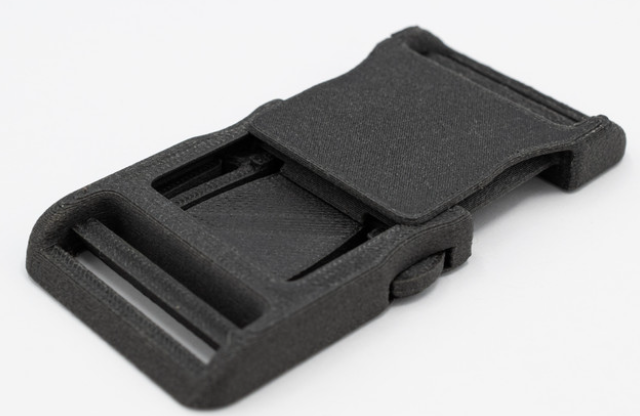

Fortis3D’s development team optimized fiber loading and processing variables to produce the “strongest” in the field
“One of the fiber-reinforced polyamide filaments with lower glass fiber content. The reduced glass fiber content enhances printing performance, reduces nozzle wear and increases surface finish. In order to still achieve a high tensile strength of 78MPa after adjustment In order to improve the tensile strength, a chemical coupling agent is additionally used to strengthen the bond between the glass fiber and the polymer matrix.
It offers over 90% retention of tensile strength compared to injection molding and is tougher than other leading brands of glass fiber and carbon fiber reinforced nylon materials. Using SnapPrint with Fortis3D compared to typical glass fiber reinforced PA6 filament
When using nylon copolymers similar to PA, the moisture absorption rate is reduced by 30%. Compared to glass fiber reinforced PA6 filaments, stringing has been reduced to a minimum even when placed under ambient conditions.
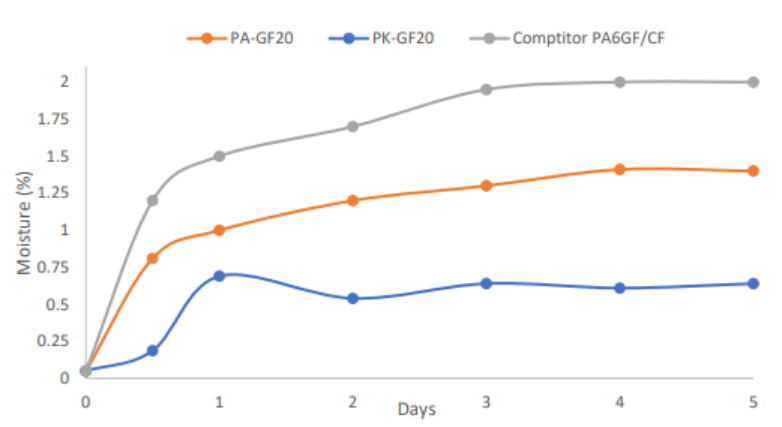
Polyketone (PK) is a terpolymer of propylene, ethylene and carbon monoxide with characteristics similar to PA12 but with reduced moisture absorption, higher chemical and impact resistance, and reduced friction and wear. It also retains mechanical strength after absorbing moisture, unlike nylon. Environmentally, polyketone production produces 60% less CO2 than nylon production. However, it is extremely difficult to print on its own due to excessive warping and lack of adhesion to most build table adhesives and materials. To solve this problem, Fortis3D’s development team created a proprietary formula that greatly reduces warping and conforms to most build table materials using only PVA glue. Chopped glass fibers are added for strength and stiffness, making this material comparable to other carbon- or glass-reinforced nylons in the industry without the danger of excessive moisture absorption. Compared with typical glass fiber reinforced PA6 filament, the hygroscopicity is reduced by about 70%, which means that under the ambient conditions of a week, the number of drawing can be limited, so that the strength of the part is not affected.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
