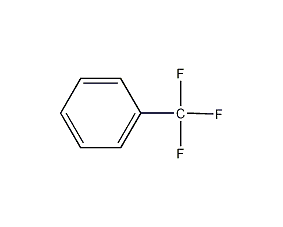
Structural formula
| Business number | 02D9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H5F3 |
| Molecular weight | 146.11 |
| label |
trifluoromethylbenzene, Benzenetrifluoromethane, Fluoroform, Benchuan trifluoride, α,α,α-trifluorotoluene, Benzotrifluoride, Benzylidynetrifluoride, Vulcanizing agent, Pesticides; pesticide intermediates, Aromatic halogen derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:98-08-8
MDL number:MFCD00000372
EINECS number:202-635-0
RTECS number:XT9450000
BRN number:1906908
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with aromatic odor.
2. Boiling point (ºC): 104
3. Melting point (ºC): -29.1
4. Relative density (g/mL, 25/4ºC ): 1.1812
5. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4ºC): 1.1884
6. Relative density (g/mL, 30/4ºC): 1.175
7. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 5.04
8. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.4699
9. Refractive index (n25ºC) : 1.4145
10. Kinematic viscosity (m2/s, 20ºC): 0.75×10-6
11. Kinematic viscosity (m2/s, 30ºC): 0.69×10-6
12. Flash point (closed cup, ºC): 22
13. Ignition point (ºC): None
14. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 33.95
15. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.) :32.66
16. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, gas): -581.13
17. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, liquid): -618.809×103
18. Heat of combustion (KJ/g): -23.1
19. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 13.79
20. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 1×10-7
21. Solubility (%, water, room temperature): 0.045
22. Vapor pressure (kPa, 55ºC): 19.92
23. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 30~40ºC): 0.00121
24. Solubility : Insoluble in water, miscible with alcohol, acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, ether, hexane, etc. Can dissolve most organic compounds.
25. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 16.654
26. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.780×109
27. van der Waals volume ( cm3·mol-1): 67.170
28. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -599.15
29. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 372.70
30. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -510.35
31. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1 sup>·K-1): 130.42
32. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -636.72
33. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 271.50
34. Liquid Phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -517.81
35. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1· K-1): 190.8
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 15mg/kg; Rat inhalation LC50: 70810 mg/m3/4H; Mouse oral LD50: 10000mg/kg; Mouse inhalation LC50: 92240 mg/m3/2H; small Rat peritoneal cavity LD50: 100mg/kg; Amphibian-frog subcutaneous LDL0: 870mg/kg; Mammal inhalation LC50: 92mg/m3; 2. Low toxicity, can damage the central nervous system when taken orally in large amounts. 3. Irritating to the skin. Inhaling excessive concentrations of vapor can have an anesthetic effect on the central nervous system. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 2.5mg/m3.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 31.23
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 122.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 264.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 21.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 12.38
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 99.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters Number: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants, strong alkalis, and strong reducing agents. It is thermally stable and does not change when heated to 300°C in the presence of iron or copper. Hydrolysis with sulfuric acid produces benzoic acid. Hydrolysis can also occur with hydrofluoric acid. Trifluorotoluene can also undergo nitration and sulfonation reactions.
2.This product is poisonous! Affects the central nervous system, the maximum allowable concentration in the air (measured as fluorine) is 2.5mg/m3. The operating area should be well ventilated. Operators should wear rubber gloves, respirators, and protective clothing to avoid inhaling vapors.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials. 2. When this product encounters high heat, it will burn in an open flame and decompose when heated to release toxic fluoride gas. Can react strongly with oxidants. It should be stored in a cool and ventilated warehouse with a temperature not exceeding 30°C, away from fires and heat sources, and away from direct sunlight. It should be stored in separate warehouses from oxidants. It should be loaded and unloaded with care during transportation to prevent damage to the packaging. It is a Class 1 flammable liquid with hazardous regulation number 61044.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of ω, ω, ω-trichlorotoluene and anhydrous hydrogen fluoride. The molar ratio of ω, ω, ω-trichlorotoluene and anhydrous hydrogen fluoride is 1:3.88. The reaction is carried out at a temperature of 80-104°C and a pressure of 1.67-1.77MPa for 2-3 hours. The yield is 72.1%. Because anhydrous hydrogen fluoride is cheap and easy to obtain, the equipment is easy to solve, no special steel is required, the cost is low, and it is suitable for industrialization.
![]()
2. From ω,ω, Obtained from the interaction between ω-trifluorotoluene and antimony trifluoride. Place ωωω trifluoromethylbenzene and antimony trifluoride in a reaction pot for heating and distillation, and the distillate is crude trifluoromethylbenzene. Wash with 5% hydrochloric acid, add 5% sodium hydroxide solution, heat and distill, and collect the 80-105°C fraction. The upper liquid was separated, and the lower liquid was dried with anhydrous calcium chloride and filtered to obtain trifluoromethylbenzene. The yield is 75%. This method consumes antimony compounds and has a high cost. It is generally only used under laboratory conditions and is more convenient.
3. The preparation method is to use toluene as raw material, first chlorine the side chain with chlorine in the presence of a catalyst to obtain α, α, α-trichlorotoluene, and then react with hydrogen fluoride to obtain the product.
Purpose
Used as raw materials for intermediates such as pesticides, medicines, and dyes, and in the manufacture of vulcanizing agents, insecticides, solvents, and insulating oils.
Thermal distillation, the distillate is crude trifluoromethylbenzene. Wash with 5% hydrochloric acid, add 5% sodium hydroxide solution, heat and distill, and collect the 80-105°C fraction. The upper liquid was separated, and the lower liquid was dried with anhydrous calcium chloride and filtered to obtain trifluoromethylbenzene. The yield is 75%. This method consumes antimony compounds and has a high cost. It is generally only used under laboratory conditions and is more convenient.
3. The preparation method is to use toluene as raw material, first chlorine the side chain with chlorine in the presence of a catalyst to obtain α, α, α-trichlorotoluene, and then react with hydrogen fluoride to obtain the product.
Purpose
Used as raw materials for intermediates such as pesticides, medicines, and dyes, and in the manufacture of vulcanizing agents, insecticides, solvents, and insulating oils.



 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏
